Detection of Electroencephalographic Abnormalities and Its Associated Factors among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in Thailand
- PMID: 36292416
- PMCID: PMC9601834
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10101969
Detection of Electroencephalographic Abnormalities and Its Associated Factors among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in Thailand
Abstract
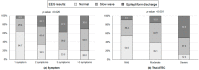
Epilepsy often causes more severe behavioral problems in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and is strongly associated with poor cognitive functioning. Interestingly, individuals with ASD without a history of epilepsy can have abnormal electroencephalographic (EEG) activity. The aim of this study was to examine associations between EEG abnormalities and the ASD severity in children. The children with ASD who enrolled at the Rajanagarindra Institute of Child Development, Thailand were included in this study. The severity of ASD was measured by interviewing their parents with the Thai autism treatment evaluation checklist. The short sensory profile checklist was used for screening the abnormality of children in each domain. Ordinal logistic regression analysis was used to examine associations between factors potentially linked to EEG abnormalities. Most of the study participants were boys (87.5%) and the median age was 5 years. Among the 128 children, 69.5% showed EEG abnormalities (41.4% slow-wave and 28.1% epileptiform-discharge). The results show that a larger number of symptoms and increased severity of ASD were independently associated with a higher risk of EEG abnormalities. Our results emphasize the need for guidelines on the presence of EEG abnormalities in children with ASD for the early detection of epilepsy and improving treatment outcomes.
Keywords: EEG abnormalities; Thai autism treatment evaluation checklist; autism spectrum disorder; electroencephalography; epilepsy; short sensory profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5™. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.; Arlington, VA, USA: 2013.
-
- Plubrukarn R., Piyasil V., Moungnoi P., Tanprasert S., Chutchawalitsakul V. Trend study of autistic spectrum disorders at Queen Sirikit National Institute of Child Health. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2005;88:891–897. - PubMed
-
- Hansakunachai T., Roongpraiwan R., Sombuntham T., Limprasert P., Ruangdaraganon N. A new structured interview for children with autism spectrum disorder based on the DSM-IV. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2014;97:S7–S14. - PubMed
-
- Autism at a Glance in Asean under the Autism Mapping Project in the Asean Region Part II. [(accessed on 7 October 2021)]. Available online: https://www.apcdfoundation.org/th/node/118/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

