Confounding Factors Impacting microRNA Expression in Human Saliva: Methodological and Biological Considerations
- PMID: 36292760
- PMCID: PMC9602126
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13101874
Confounding Factors Impacting microRNA Expression in Human Saliva: Methodological and Biological Considerations
Abstract
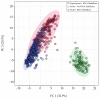
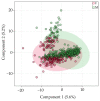
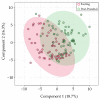
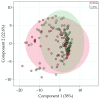
There is growing interest in saliva microRNAs (miRNAs) as non-invasive biomarkers for human disease. Such an approach requires understanding how differences in experimental design affect miRNA expression. Variations in technical methodologies, coupled with inter-individual variability may reduce study reproducibility and generalizability. Another barrier facing salivary miRNA biomarker research is a lack of recognized "control miRNAs". In one of the largest studies of human salivary miRNA to date (922 healthy individuals), we utilized 1225 saliva samples to quantify variability in miRNA expression resulting from aligner selection (Bowtie1 vs. Bowtie2), saliva collection method (expectorated vs. swabbed), RNA stabilizer (presence vs. absence), and individual biological factors (sex, age, body mass index, exercise, caloric intake). Differential expression analyses revealed that absence of RNA stabilizer introduced the greatest variability, followed by differences in methods of collection and aligner. Biological factors generally affected a smaller number of miRNAs. We also reported coefficients of variations for 643 miRNAs consistently present in saliva, highlighting several salivary miRNAs to serve as reference genes. Thus, the results of this analysis can be used by researchers to optimize parameters of salivary miRNA measurement, exclude miRNAs confounded by numerous biologic factors, and identify appropriate miRNA controls.
Keywords: biomarker; housekeeping; miRNA; salivary; stabilizer.
Conflict of interest statement
S.D.H. serves as a paid consultant and scientific advisory board member for Quadrant Biosciences and Spectrum Solutions LLC, who had no role in the design of the study; in the analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery and prevalidation of salivary extracellular microRNA biomarkers panel for the noninvasive detection of benign and malignant parotid gland tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 1;19(11):3032-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3505. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23575476
-
Refinement of saliva microRNA biomarkers for sports-related concussion.J Sport Health Sci. 2023 May;12(3):369-378. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2021.08.003. Epub 2021 Aug 28. J Sport Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 34461327 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary miRNA Expression in Children With Persistent Post-concussive Symptoms.Front Public Health. 2022 May 30;10:890420. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.890420. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35712307 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary microRNAs and oral cancer detection.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;936:313-24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-083-0_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23007518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Salivary miRNome: A Promising Biomarker of Disease.Microrna. 2021;10(1):29-38. doi: 10.2174/2211536610666210412154455. Microrna. 2021. PMID: 33845754 Review.
Cited by
-
Obtaining miRNA from Saliva-Comparison of Sampling and Purification Methods.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 25;24(3):2386. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032386. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768706 Free PMC article.
-
Spitting in the wind?-The challenges of RNA sequencing for biomarker discovery from saliva.Int J Legal Med. 2024 Mar;138(2):401-412. doi: 10.1007/s00414-023-03100-3. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Int J Legal Med. 2024. PMID: 37847308 Free PMC article.
-
Review on the Role of Salivary Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Post-Concussion Syndrome.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Apr 7;13(8):1367. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13081367. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37189468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preliminary Evidence for Neuronal Dysfunction Following Adverse Childhood Experiences: An Investigation of Salivary MicroRNA Within a High-Risk Youth Sample.Genes (Basel). 2024 Nov 4;15(11):1433. doi: 10.3390/genes15111433. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39596633 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miRNAs as Biomarkers of Ischemic Stroke.Brain Sci. 2023 Nov 27;13(12):1647. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13121647. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 38137095 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Corey-Bloom J., Fischer R.S., Kim A., Snell C., Parkin G.M., Granger D.A., Granger S.W., Thomas E.A. Levels of Interleukin-6 in Saliva, but Not Plasma, Correlate with Clinical Metrics in Huntington’s Disease Patients and Healthy Control Subjects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:6363. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176363. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beversdorf D.Q., Sohl K., Levitskiy D., Tennant P., Goin-Kochel R.P., Shaffer R.C., Confair A., Middleton F.A., Hicks S.D. Saliva RNA Biomarkers of Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Children With Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Potential Implications for Precision Medicine. Front. Psychiatry. 2022;12:27. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.824933. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mager D.L., Haffajee A.D., Delvin P.M., Norris C.M., Posner M.R., Goodson J.M. The salivary microbiota as a diagnostic indicator of oral cancer: A descriptive, non-randomized study of cancer-free and oral squamous cell carcinoma subjects. J. Transl. Med. 2005;3:27. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-3-27. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

