Lipase Catalyzed Transesterification of Model Long-Chain Molecules in Double-Shell Cellulose-Coated Oil-in-Water Emulsion Particles as Microbioreactors
- PMID: 36292979
- PMCID: PMC9603428
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232012122
Lipase Catalyzed Transesterification of Model Long-Chain Molecules in Double-Shell Cellulose-Coated Oil-in-Water Emulsion Particles as Microbioreactors
Abstract
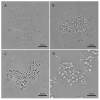
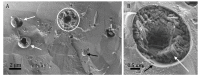
Lipase-catalyzed transesterification is prevalent in industrial production and is an effective alternative to chemical catalysis. However, due to lipases' unique structure, the reaction requires a biphasic system, which suffers from a low reaction efficiency caused by a limited interfacial area. The use of emulsion particles was found to be an effective way to increase the surface area and activity. This research focuses on cellulose as a natural surfactant for oil-in-water emulsions and evaluates the ability of lipase, introduced into the emulsion's aqueous phase, to integrate with the emulsion microparticles and catalyze the transesterification reaction of high molecular weight esters dissolved in the particles' cores. Cellulose-coated emulsion particles' morphology was investigated by light, fluorescence and cryogenic scanning electron microscopy, which reveal the complex emulsion structure. Lipase activity was evaluated by measuring the hydrolysis of emulsified p-nitrophenyl dodecanoate and by the transesterification of emulsified methyl laurate and oleyl alcohol dissolved in decane. Both experiments demonstrated that lipase introduced in the aqueous medium can penetrate the emulsion particles, localize at the inner oil core interface and perform effective catalysis. Furthermore, in this system, lipase successfully catalyzed a transesterification reaction rather than hydrolysis, despite the dominant presence of water.
Keywords: cellulose; emulsions; lipase; transesterification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Canet A., Bonet-Ragel K., Benaiges M.D., Valero F. Lipase-catalysed transesterification: Viewpoint of the mechanism and influence of free fatty acids. Biomass Bioenergy. 2016;85:94–99. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2015.11.021. - DOI
-
- Cao X., Xu H., Li F., Zou Y., Ran Y., Ma X., Cao Y., Xu Q., Qiao D., Cao Y. One-step direct transesterification of wet yeast for biodiesel production catalyzed by magnetic nanoparticle-immobilized lipase. Renew. Energy. 2021;171:11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.02.065. - DOI
-
- Park K.M., Jo S.K., Yu H., Park J.Y., Choi S.J., Lee C.J., Chang P.S. Erythorbyl laurate as a potential food additive with multi-functionalities: Antibacterial activity and mode of action. Food Control. 2018;86:138–145. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.11.008. - DOI
-
- Lue B.M., Karboune S., Yeboah F.K., Kermasha S. Lipase-catalyzed esterification of cinnamic acid and oleyl alcohol in organic solvent media. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005;80:462–468. doi: 10.1002/jctb.1237. - DOI
-
- Gunawan E.R., Basri M., Rahman M.B.A., Salleh A.B., Rahman R.N.Z.A. Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Palm-Based Wax Esters. J. Oleo Sci. 2004;53:471–477. doi: 10.5650/jos.53.471. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

