NAC1 Maintains Root Meristem Activity by Repressing the Transcription of E2Fa in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 36293114
- PMCID: PMC9603599
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232012258
NAC1 Maintains Root Meristem Activity by Repressing the Transcription of E2Fa in Arabidopsis
Abstract
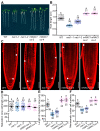
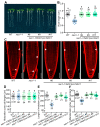
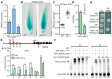
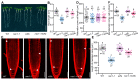
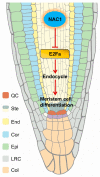
Root meristem is a reserve of undifferentiated cells which guide root development. To maintain root meristem identity and therefore continuous root growth, the rate of cell differentiation must coordinate with the rate of generation of new cells. The E2 promoter-binding factor a (E2Fa) has been shown to regulate root growth through controlling G1/S cell cycle transitions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Here, we found that NAC1, a member of the NAM/ATAF/CUC family of transcription factors, regulated root growth by directly repressing the transcription of E2Fa. Loss of NAC1 triggers an up-regulation of the E2Fa expression and causes a reduced meristem size and short-root phenotype, which are largely rescued by mutation of E2Fa. Further analysis showed that NAC1 was shown to regulate root meristem by controlling endopolyploidy levels in an E2Fa-dependent manner. This study provides evidence to show that NAC1 maintains root meristem size and root growth by directly repressing the transcription of E2Fa in Arabidopsis.
Keywords: E2Fa; NAC1; endoreduplication; meristem; root.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis E2FA stimulates proliferation and endocycle separately through RBR-bound and RBR-free complexes.EMBO J. 2012 Mar 21;31(6):1480-93. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.13. Epub 2012 Feb 3. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22307083 Free PMC article.
-
Auxin-dependent cell cycle reactivation through transcriptional regulation of Arabidopsis E2Fa by lateral organ boundary proteins.Plant Cell. 2011 Oct;23(10):3671-83. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.088377. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 22003076 Free PMC article.
-
E2Fb and E2Fa transcription factors independently regulate the DNA damage response after ultraviolet B exposure in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2022 Mar;109(5):1098-1115. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15616. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Plant J. 2022. PMID: 34859915
-
NAC1 regulates root ground tissue maturation by coordinating with the SCR/SHR-CYCD6;1 module in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant. 2023 Apr 3;16(4):709-725. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2023.02.006. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Mol Plant. 2023. PMID: 36809880
-
Root development-two meristems for the price of one?Curr Top Dev Biol. 2010;91:67-102. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(10)91003-X. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20705179 Review.
Cited by
-
NACs, generalist in plant life.Plant Biotechnol J. 2023 Dec;21(12):2433-2457. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14161. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Plant Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37623750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Arabidopsis Seedlings Under Heat Stress on Whole Plants, Shoots, and Roots Reveals New HS-Regulated Genes, Organ-Specific Responses, and Shoots-Roots Communication.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 10;26(6):2478. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062478. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141121 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of regulating the growth and development of tomato seedlings by the crosstalk between JA and TOR signaling.Plant Cell Rep. 2025 Mar 24;44(4):82. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03476-z. Plant Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40126670
-
Genome-Wide Identification of NAC Family Genes and Their Expression Analyses in Response to Osmotic Stress in Cannabis sativa L.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 30;25(17):9466. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179466. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273412 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Transcriptional and Metabolomic Analysis of Factors Influencing Root Tuber Enlargement during Early Sweet Potato Development.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 14;15(10):1319. doi: 10.3390/genes15101319. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457443 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

