CPAP Influence on Readily Available Inflammatory Markers in OSA-A Pilot Study
- PMID: 36293288
- PMCID: PMC9604000
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232012431
CPAP Influence on Readily Available Inflammatory Markers in OSA-A Pilot Study
Abstract
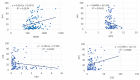
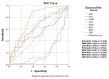
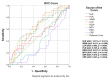
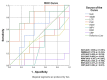
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is characterized by repetitive upper airway collapse, chronic hypoxia and a proinflammatory phenotype. The purpose of our study was to evaluate readily available inflammatory biomarkers (C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), white blood cell count (WBC), red cell distribution width (RDW), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), mean platelet volume (MPV), WBC-to-MPV ratio (WMR) and lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio (LCR)) before and after CPAP in patients with moderate-severe OSA. We performed a prospective study that included patients with newly-diagnosed moderate-severe OSA. The control groups (patients without OSA and with mild OSA) were selected from the hospital polygraphy database. All subjects underwent routine blood panel, which was repeated in moderate-severe OSA patients after 8 weeks of CPAP. Our final study group included 31 controls, 33 patients with mild, 22 patients with moderate and 37 patients with severe OSA. CRP, ESR, NLR and WMR were correlated with OSA severity. After 8-week CPAP therapy, we documented a decrease in weight status, which remained statistically significant in both CPAP-adherent and non-adherent subgroups. Readily available, inexpensive inflammatory parameters can predict the presence of moderate-severe OSA, but are not influenced by short-term CPAP.
Keywords: C-reactive protein (CRP); continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP); inflammation; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR); obstructive sleep apnea (OSA); platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR); red cell distribution width (RDW).
Conflict of interest statement
M.R. and D.B. have received financial support for conference attendance from Linde Gas and Vital Aire.
Figures

References
-
- Heinzer R., Vat S., Marques-Vidal P., Marti-Soler H., Andries D., Tobback N., Mooser V., Preisig M., Malhotra A., Waeber G., et al. Prevalence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in the General Population: The HypnoLaus Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015;3:310–318. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00043-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jullian-Desayes I., Joyeux-Faure M., Tamisier R., Launois S., Borel A.-L., Levy P., Pepin J.-L. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Treatment by Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Cardiometabolic Biomarkers: A Systematic Review from Sham CPAP Randomized Controlled Trials. Sleep Med. Rev. 2015;21:23–38. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2014.07.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

