Exploring the Absorption Mechanisms of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids to Epigallocatechin Gallate
- PMID: 36293456
- PMCID: PMC9604465
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232012600
Exploring the Absorption Mechanisms of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids to Epigallocatechin Gallate
Abstract
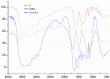
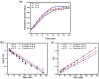
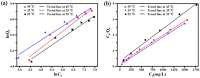
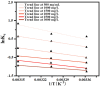
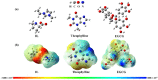
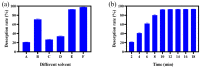
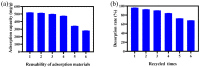
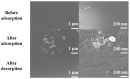
Imidazolium-based ionic liquids are wildly used in natural product adsorption and purification. In this work, one typical polymeric ionic liquid (PIL) was synthesized by using L-proline as the anion, which exhibited excellent adsorption capacity toward tea polyphenol epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). The adsorption conditions were optimized with the response surface method (RSM). Under the optimum conditions, the adsorption capacity of the PIL for EGCG can reach as high as 552 mg/g. Dynamics and isothermal research shows that the adsorption process of EGCG by the PIL particularly meets the quasi-second-order kinetic equation and monolayer adsorption mechanism. According to thermodynamic parameter analysis, the adsorption process is endothermic and spontaneous. The results of theoretical calculation by molecular docking also demonstrated the interaction mechanisms between EGCG and the ionic liquid. Considering the wide application of imidazolium-based ionic liquids in component adsorption and purification, the present study can not only be extended to other similar experimental mechanism validation, but also be representative for guiding the synthesis of PIL and optimization of adsorption conditions.
Keywords: epigallocatechin gallate; ionic liquids; mechanism; molecular docking; polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Synthesis of a New Imidazole Amino Acid Ionic Liquid Polymer and Selective Adsorption Performance for Tea Polyphenols.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Sep 23;12(10):2171. doi: 10.3390/polym12102171. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32977417 Free PMC article.
-
Ionic liquid@β-cyclodextrin-gelatin composite membrane for effective separation of tea polyphenols from green tea.Food Chem. 2020 Dec 15;333:127534. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127534. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 32673948
-
Synthesis of a polymeric imidazolium-embedded octadecyl ionic liquid-grafted silica sorbent for extraction of flavonoids.J Chromatogr A. 2019 Nov 22;1606:460376. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460376. Epub 2019 Jul 18. J Chromatogr A. 2019. PMID: 31345620
-
Imidazolium based ionic liquids modified polysaccharides for adsorption and solid-phase extraction applications: A review.Carbohydr Polym. 2022 Dec 15;298:120138. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120138. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Carbohydr Polym. 2022. PMID: 36241304 Review.
-
New insights into the mechanisms of polyphenols beyond antioxidant properties; lessons from the green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin 3-gallate.Redox Biol. 2014 Jan 10;2:187-95. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.12.022. eCollection 2014. Redox Biol. 2014. PMID: 24494192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigallocatechin gallate attenuated high glucose-induced pancreatic beta cell dysfunction by modulating DRP1-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis pathways.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 22;14(1):16809. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67867-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39039202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang L., Gong L.H., Chen C.J., Han H.B., Li H.H. Column-chromatographic extraction and separation of polyphenols, caffeine and theanine from green tea. Food Chem. 2012;131:1539–1545. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.129. - DOI
-
- Dong W.B., Hu Y., Zhang J.H. Study on the Process of Preparation of TPs by Adsorption Resin Method. Food Sci. 2002;23:68–73.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

