Pharmacological and Therapeutic Applications of Esculetin
- PMID: 36293500
- PMCID: PMC9604018
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232012643
Pharmacological and Therapeutic Applications of Esculetin
Abstract
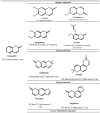
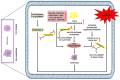
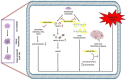
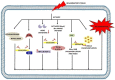
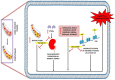
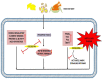
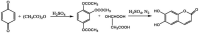
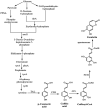
Esculetin is a coumarin compound, which belongs to the class of benzopyrone enriched in various plants such as Sonchus grandifolius, Aesculus turbinata, etc. Free radicals lead to the development of oxidative stress causing inflammation, arthritis, cancer, diabetes, fatty liver disease, etc. These further reduce the efficacy of anticancer drugs, activate inflammatory signaling pathways, degrade joints and cartilage, and disrupt the glycemic index and normal function of liver enzymes. For instance, the current treatment modalities used in arthritis such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, disease-modifying anti-rheumatoid drugs, and lipoxygenase inhibitors present limited efficacy and adverse effects. Thus, there is a constant need to find newer and safer alternatives. Esculetin has an immense antioxidative potential thereby alleviating arthritis, diabetes, malignancies, and hepatic disorders. Structurally, esculetin contains two hydroxyl groups, which enhance its ability to function as an antioxidant by inhibiting oxidative stress in pathological conditions. Leukotriene B4 synthesis, NF-κB and MPAK pathway activation, and inflammatory cytokine production are the main causes of bone and joint deterioration in arthritis, whereas esculetin treatment reverses these factors and relieves the disease condition. In contrast, lipid peroxidation caused by upregulation of TGF-β-mediated expression and dysfunction of antioxidant enzymes is inhibited by esculetin therapy, thus reducing liver fibrosis by acting on the PI3K/FoxO1 pathway. Therefore, targeting NF-κB, pro-inflammatory cytokines, TGF-β and oxidative stress may be a therapeutic strategy to alleviate arthritis and liver fibrosis.
Keywords: arthritis; cancer; chromatography; diabetes; esculetin; fatty liver; inflammation; oxidative stress; pharmacokinetic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

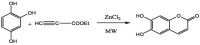
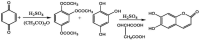
References
-
- Vuolo M.M., Lima V.S., Junior M.R.M. Bioactive Compounds: Health Benefits and Potential Applications. Woodhead Publishing; Sawston, UK: 2019. Chapter 2—Phenolic Compounds: Structure, Classification, and Antioxidant Power; pp. 33–50.
-
- Kotamraju S., Chitambar C.R., Kalivendi S.V., Joseph J., Kalyanaraman B. Transferrin receptor-dependent iron uptake is responsible for doxorubicin-mediated apoptosis in endothelial cells: Role of oxidant-induced iron signaling in apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:17179–17187. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111604200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

