Mixture Risk Assessment of Complex Real-Life Mixtures-The PANORAMIX Project
- PMID: 36293571
- PMCID: PMC9602166
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192012990
Mixture Risk Assessment of Complex Real-Life Mixtures-The PANORAMIX Project
Abstract
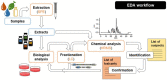
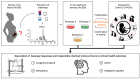
Humans are involuntarily exposed to hundreds of chemicals that either contaminate our environment and food or are added intentionally to our daily products. These complex mixtures of chemicals may pose a risk to human health. One of the goals of the European Union's Green Deal and zero-pollution ambition for a toxic-free environment is to tackle the existent gaps in chemical mixture risk assessment by providing scientific grounds that support the implementation of adequate regulatory measures within the EU. We suggest dealing with this challenge by: (1) characterising 'real-life' chemical mixtures and determining to what extent they are transferred from the environment to humans via food and water, and from the mother to the foetus; (2) establishing a high-throughput whole-mixture-based in vitro strategy for screening of real-life complex mixtures of organic chemicals extracted from humans using integrated chemical profiling (suspect screening) together with effect-directed analysis; (3) evaluating which human blood levels of chemical mixtures might be of concern for children's development; and (4) developing a web-based, ready-to-use interface that integrates hazard and exposure data to enable component-based mixture risk estimation. These concepts form the basis of the Green Deal project PANORAMIX, whose ultimate goal is to progress mixture risk assessment of chemicals.
Keywords: PANORAMIX; developmental neurotoxicity; effect-based trigger values; effect-directed analysis; mixture risk assessment; new methodological approaches; real-life mixtures; reproductive toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. The companies had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Apel P., Kortenkamp A., Koch H.M., Vogel N., Rüther M., Kasper-Sonnenberg M., Conrad A., Brüning T., Kolossa-Gehring M. Time Course of Phthalate Cumulative Risks to Male Developmental Health over a 27-Year Period: Biomonitoring Samples of the German Environmental Specimen Bank. Environ. Int. 2020;137:105467. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105467. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Neale P.A., Braun G., Brack W., Carmona E., Gunold R., König M., Krauss M., Liebmann L., Liess M., Link M., et al. Assessing the Mixture Effects in in Vitro Bioassays of Chemicals Occurring in Small Agricultural Streams during Rain Events. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020;54:8280–8290. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c02235. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baumer A., Jäsch S., Ulrich N., Bechmann I., Landmann J., Stöver A., Escher B.I. Chemical Mixtures in Human Post-Mortem Tissues Assessed by a Combination of Chemical Analysis and in Vitro Bioassays after Extraction with Silicone. Environ. Int. 2021;157:106867. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106867. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

