A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Different Training Modalities on the Inflammatory Response in Adolescents with Obesity
- PMID: 36293806
- PMCID: PMC9603579
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192013224
A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Different Training Modalities on the Inflammatory Response in Adolescents with Obesity
Abstract
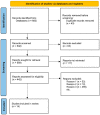
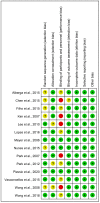
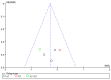
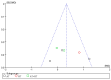
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of different training modalities on improving the inflammatory response in adolescents with obesity. For the study methodology, the databases such as China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Data, Pubmed, Web of Science, and EBSCO were selected for searching. The methodological quality of the included studies was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias (ROB) tool, and statistical analysis was performed by applying RevMan 5.4.1 analysis software. A total of 14 studies with 682 subjects were included. The results of this meta-analysis showed that aerobic training (AT) and aerobic plus resistance training (AT + RT) reduced the levels of IL-6 and CRP in adolescents with obesity. Among them, AT + RT was more effective than other training modalities in reducing IL-6 and CRP in adolescents with obesity. Different training modalities have no effect on the TNF-α level in adolescents with obesity. However, regarding the increase in IL-6, CRP, and TNF-α in adolescents with obesity, resistance training (RT) did not lead to significant differences. In conclusion, long-term regular AT, AT + RT, and HIIT are all helpful in improving the inflammatory state of adolescents with obesity, with AT + RT being the best training modality to combat inflammation in adolescents with obesity.
Keywords: adolescents; inflammation; meta-analysis; obese; training modalities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Meta-Analysis of the Influence on Inflammatory Factors in Type 2 Diabetes among Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients by Various Exercise Modalities.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 18;20(3):1783. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031783. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Different Exercise Modes on Inflammatory Response in the Elderly.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 22;19(16):10451. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191610451. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36012088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of different exercise modalities on inflammatory markers in the obese and overweight populations: unraveling the mystery of exercise and inflammation.Front Physiol. 2024 Jun 12;15:1405094. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1405094. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38933362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of exercise training on inflammatory markers in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Physiol Behav. 2024 May 1;278:114524. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2024.114524. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Physiol Behav. 2024. PMID: 38521236
-
Effect of high-intensity interval training on cardiometabolic risk factors in childhood obesity: a meta-analysis.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2021 May;61(5):743-752. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.20.11329-X. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2021. PMID: 33975429
Cited by
-
Effects of Physical Exercise on the Microbiota in Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 11;16(16):2657. doi: 10.3390/nu16162657. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of exercise training on glucose metabolism indicators and inflammatory markers in obese children and adolescents: A meta-analysis.World J Diabetes. 2024 Jun 15;15(6):1353-1366. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i6.1353. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38983830 Free PMC article.
-
The intensity of exercise and inflammation markers in women with overweight & obesity: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Int J Obes (Lond). 2025 Jul;49(7):1229-1239. doi: 10.1038/s41366-025-01777-7. Epub 2025 May 16. Int J Obes (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40379914
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

