Work Ability and Quality of Life in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 36293837
- PMCID: PMC9603111
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192013260
Work Ability and Quality of Life in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Background: Reduced work participation has social implications (sickness absence, economic impact) and consequences for the individual patient (impoverishment, depression, limited social interaction). As patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are more likely to experience job loss and/or at-work productivity loss and are at higher risk of sickness absence and, ultimately, permanent work productivity, consideration should be given to the association between work productivity or partial work capacity and quality of life (QoL). The aim of the study was to assess the relationship between QoL and the risk of work disability, as well as to estimate the risk of a future event and identify factors affecting the risk of work disability in RA inpatients.
Material and methods: This cross-sectional study included 142 inpatients (65 male) aged 47 (38-58) years, who met the established criteria for a diagnosis of RA and treatment with biologic drugs. Only standardized tools were used to examine the patients: WHOQOL-BREF, MFIS and AS-WIS.
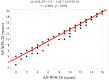
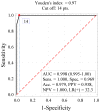
Results: An analysis of the QoL scores on the WHOQOL-BREF demonstrated that the patients' QoL was lowest in the physical health domain and highest in the social relationships domain. The median WHOQOL-BREF total score in the group studied was 62.8, which indicates a moderate QoL. The median total score for the risk of work disability (AS-WIS) was 10.1, which indicates that the level of risk of work disability in the patients was higher than the average level reported in the literature. A multivariate analysis showed that the following were significant independent determinants of a higher risk of work disability: low QoL in the WHOQOL-BREF physical health (β = 0.961; p = 0.029) and psychological health (β = 1.752; p = 0.002) domains, being in a relationship (β = 0.043; p = 0.005) and the use of opioids for pain (β = 3.054; p = 0.012).
Conclusions: RA patients presented with moderate QoL, moderate fatigue (MFIS) and high risk of disability (AS-WIS). There is an association between a high risk of work disability and lower QoL, especially in the physical and psychological health domains. The lower the QoL in those domains, the higher the risk of work disability. The identification of factors increasing the risk of work disability will help in planning tailored interventions to improve at-work productivity loss and thus prevent work disability.
Keywords: fatigue; quality of life; rheumatoid arthritis; work.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between Malnutrition and Quality of Life in Elderly Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Nutrients. 2021 Apr 12;13(4):1259. doi: 10.3390/nu13041259. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33921207 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep Disturbance and Quality of Life in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Prospective mHealth Study.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Apr 22;24(4):e32825. doi: 10.2196/32825. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 35451978 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Biological Therapeutics on Patient-Reported Quality-Of-Life Outcomes (Whoqol-Bref), Functional Scores and Disease Activity among Croatian Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Our Experience.Psychiatr Danub. 2020 Nov;32(Suppl 4):547-552. Psychiatr Danub. 2020. PMID: 33212462
-
Newer biological agents in rheumatoid arthritis: impact on health-related quality of life and productivity.Drugs. 2010;70(2):121-45. doi: 10.2165/11531980-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20108988 Review.
-
Impact of Biological Therapies on Quality of Life in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Narrative Review.Open Access Rheumatol. 2025 Apr 23;17:73-86. doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S523778. eCollection 2025. Open Access Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40291770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Women's sexual health improvement: sexual quality of life and pelvic floor muscle assessment in asymptomatic women.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 21;11:1289418. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1289418. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38449880 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting work ability impairment in post COVID-19 patients: a machine learning model based on clinical parameters.Infection. 2025 Jun;53(3):1189-1197. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02459-8. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Infection. 2025. PMID: 39821741 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine-Rich Repeat Containing 15 Promotes the Inflammatory Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating NF-κB Pathway.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025 Jul;13(7):e70220. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70220. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025. PMID: 40642947 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased muscle strength in adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis animal model: A relationship to behavioural assessments.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 3;10(1):e23264. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23264. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38163119 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of WeChat platform-based continuing care on self-management and quality of life in patients with arthritis: A quasi-experimental study.Digit Health. 2023 Sep 18;9:20552076231197104. doi: 10.1177/20552076231197104. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2023. PMID: 37732135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sokka T., Kautiainen H., Pincus T., Verstappen S.M., Aggarwal A., Alten R., Andersone D., Badsha H., Baecklund E., Belmonte M., et al. Work disability remains a major problem in rheumatoid arthritis in the 2000s: Data from 32 countries in the QUEST-RA study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010;12:R42. doi: 10.1186/ar2951. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kwiatkowska B., Raciborski F., Maślińska M., Kłak A., Gryglewicz J., Samel-Kowalik P. Wczesna Diagnostyka Chorób reumatycznych—Ocena Obecnej Sytuacji i Rekomendacje Zmian. [(accessed on 2 October 2022)]. Available online: https://spartanska.pl/wp-content/uploads/raport_wczesna_diagnostyka_ChR.pdf.
-
- Gierczyński J. Absencja Chorobowa Pracujących Jako Problem Ubezpieczeniowy—Porównanie Sytuacji w Polsce i w Wielkiej Brytanii [Eng. Sickness Absence as an Insurance Problem—Comparison of the Situation in Poland with the UK] [(accessed on 2 October 2022)]. Available online: https://piu.org.pl/public/upload/ibrowser/WU/WU3_2014/04%20gierczynski_1....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

