COVID-19 Vaccines on TikTok: A Big-Data Analysis of Entangled Discourses
- PMID: 36293868
- PMCID: PMC9602594
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192013287
COVID-19 Vaccines on TikTok: A Big-Data Analysis of Entangled Discourses
Abstract
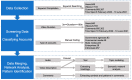
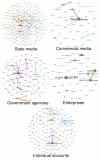
Focusing on social media affordances and China's social/political context, the present study analyzed the digital communication practices about COVID-19 vaccines on a popular social media platform-TikTok-which is called DouYin in China. Overall, this study identified five major forces partaking in constructing the discourses, with government agencies and state media being the dominant contributors. Furthermore, video posters demonstrated different patterns of utilizing social media affordances (e.g., hashtags) in disseminating their messages. The top hashtags adopted by state media were more representative of international relations and Taiwan; those by government agencies were of updates on pandemic outbreaks; those by individual accounts were of mainstream values and health education; those by commercial media were of celebrities and health education; those by enterprise accounts were of TikTok built-in marketing hashtags. The posted videos elicited both cognitive and affective feedback from online viewers. Implications of the findings were discussed in the context of health communication and global recovery against the backdrop of the COVID-19 pandemic and Chinese culture.
Keywords: China; TikTok; big data; health communication; social media; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Communicating COVID-19 information on TikTok: a content analysis of TikTok videos from official accounts featured in the COVID-19 information hub.Health Educ Res. 2021 Jul 12;36(3):261-271. doi: 10.1093/her/cyab010. Health Educ Res. 2021. PMID: 33667311 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the vaccine conversation on TikTok in Italy: beyond classic vaccine stances.BMC Public Health. 2023 May 12;23(1):880. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15748-y. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37173677 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Driving Citizen Engagement With Government TikTok Accounts During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Model Development and Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Feb 4;23(2):e21463. doi: 10.2196/21463. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33481756 Free PMC article.
-
Using TikTok for public and youth mental health - A systematic review and content analysis.Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2023 Jan;28(1):279-306. doi: 10.1177/13591045221106608. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 35689365 Free PMC article.
-
Instilling Confidence in the COVID-19 Vaccine.Nurs Clin North Am. 2023 Mar;58(1):77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2022.11.001. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Nurs Clin North Am. 2023. PMID: 36731961 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 and Public Health: Analysis of Opinions in Social Media.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 5;20(2):971. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20020971. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36673729 Free PMC article.
-
The Normalization of Vaping on TikTok Using Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, and Qualitative Thematic Analysis: Mixed Methods Study.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Sep 11;26:e55591. doi: 10.2196/55591. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39259963 Free PMC article.
-
The content quality and educational significance of early childhood caries on short video platforms.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 9;25(1):1713. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22962-3. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40346611 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-stigma narratives and emotional comfort against health crisis: a context analysis of UGC short videos from patients with COVID-19 infections.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 7;13(1):14744. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41184-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37679399 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance of Gun-Related Conversations on Twitter.Prev Sci. 2024 Feb;25(2):380-391. doi: 10.1007/s11121-023-01599-x. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Prev Sci. 2024. PMID: 37962708
References
-
- Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 2022. [(accessed on 5 October 2022)]. Available online: https://www.chinacdc.cn/
-
- Meslé M.M., Brown J., Mook P., Hagan J., Pastore R., Bundle N., Pebody R.G. Estimated number of deaths directly averted in people 60 years and older as a result of COVID-19 vaccination in the WHO European Region, December 2020 to November 2021. Eurosurveillance. 2021;26:2101021. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.47.2101021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eriksson M., Åkerlund M. Through a white lens: Black victimhood, visibility, and whiteness in the Black Lives Matter movement on TikTok. Inf. Commun. Soc. 2022;1:1–19. doi: 10.1080/1369118X.2022.2065211. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical