Exploring the Associations between Social Media Addiction and Depression: Attentional Bias as a Mediator and Socio-Emotional Competence as a Moderator
- PMID: 36294077
- PMCID: PMC9602543
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192013496
Exploring the Associations between Social Media Addiction and Depression: Attentional Bias as a Mediator and Socio-Emotional Competence as a Moderator
Abstract
Social media is used daily by a significant number of young people and can have an important influence on the well-being of its users. The aim of this study was to determine the motives for social media use among Chinese youth and whether social media addiction associates with depression. Another objective was to analyze possible mediating and moderating effects in explaining the association between social media addiction and depression. Participants were 1652 secondary school students (51.5% boys and 48.5% girls) aged 12-18 years in China. The results showed that attention bias mediated the association between social media addiction and depression when adolescents' socio-emotional competencies were low, but not as strong when their socio-emotional competencies were high. The findings not only provided theoretical support for preventing the negative effects of mobile social media addiction, but could also directly contribute to improving adolescents' quality of life.
Keywords: adolescents; anxiety; attentional bias; depression; mobile social media addiction; socio-emotional competencies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

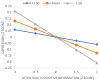
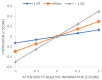
References
-
- China Internet Network Information Center The 44th China Statistical Report on Internet Development. [(accessed on 7 August 2022)];2019 Available online: http://www.cac.gov.cn/2019-08/30/c_1124938750.htm.
-
- Whiting A., Williams D. Why People Use Social Media: A Uses and Gratifications Approach. Qual. Mark. Res. Int. J. 2013;16:362–369. doi: 10.1108/QMR-06-2013-0041. - DOI
-
- Clark J.L., Algoe S.B., Green M.C. Social Network Sites and Well-Being: The role of Social Connection. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2018;27:32–37. doi: 10.1177/0963721417730833. - DOI
-
- Allen K.A., Ryan T., Gray D.L., McInerney D.M., Waters L. Social media use and social connectedness in adolescents: The positives and the potential pitfalls. Educ. Dev. Psychol. 2014;31:18–31. doi: 10.1017/edp.2014.2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

