The Dawn of a New Era in Atopic Dermatitis Treatment
- PMID: 36294465
- PMCID: PMC9605067
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11206145
The Dawn of a New Era in Atopic Dermatitis Treatment
Abstract
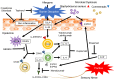
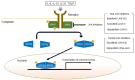
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is one of the most common chronic inflammatory skin diseases, and the condition is typified by barrier dysfunction and immune dysregulation. Recent studies have characterized various phenotypes and endotypes of AD and elucidated the mechanism. Numerous topical and systemic narrow targeting therapies for AD have been developed according to these findings. Topical medications, including Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist tapinarof, are effective and safe for AD compared to topical corticosteroids. Oral JAK inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies targeting interleukin (IL)-4, IL-13, IL-31, IL-33, OX40, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling have displayed outstanding efficacy against moderate-to-severe AD. We are currently in a new era of AD treatment.
Keywords: atopic dermatitis; biologics; small-molecule inhibitors; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chiesa Fuxench Z.C., Block J.K., Boguniewicz M., Boyle J., Fonacier L., Gelfand J.M., Grayson M.H., Margolis D.J., Mitchell L., Silverberg J.I., et al. Atopic Dermatitis in America Study: A Cross-Sectional Study Examining the Prevalence and Disease Burden of Atopic Dermatitis in the US Adult Population. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019;139:583–590. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.08.028. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

