Caspofungin Affects Extracellular Vesicle Production and Cargo in Candida auris
- PMID: 36294557
- PMCID: PMC9605528
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8100990
Caspofungin Affects Extracellular Vesicle Production and Cargo in Candida auris
Abstract
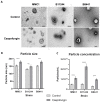
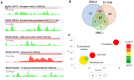
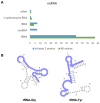
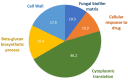
Antifungal resistance has become more frequent, either due to the emergence of naturally resistant species or the development of mechanisms that lead to resistance in previously susceptible species. Among these fungal species of global threat, Candida auris stands out for commonly being highly resistant to antifungal drugs, and some isolates are pan-resistant. The rate of mortality linked to C. auris infections varies from 28% to 78%. In this study, we characterized C. auris extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the presence of caspofungin, an echinocandin, which is the recommended first line antifungal for the treatment of infections due to this emerging pathogen. Furthermore, we also analyzed the protein and RNA content of EVs generated by C. auris cultivated with or without treatment with caspofungin. We observed that caspofungin led to the increased production of EVs, and treatment also altered the type and quantity of RNA molecules and proteins enclosed in the EVs. There were distinct classes of RNAs in the EVs with ncRNAs being the most identified molecules, and tRNA-fragments (tRFs) were abundant in each of the strains studied. We also identified anti-sense RNAs, varying from 21 to 55 nt in length. The differentially abundant mRNAs detected in EVs isolated from yeast subjected to caspofungin treatment were related to translation, nucleosome core and cell wall. The differentially regulated proteins identified in the EVs produced during caspofungin treatment were consistent with the results observed with the RNAs, with the enriched terms being related to translation and cell wall. Our study adds new information on how an echinocandin can affect the EV pathway, which is associated with the yeast cell being able to evade treatment and persist in the host. The ability of C. auris to efficiently alter the composition of EVs may represent a mechanism for the fungus to mitigate the effects of antifungal agents.
Keywords: Candida auris; RNA; drug resistance; extracellular vesicles; protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Garcia-Bustos V., Salavert M., Ruiz-Gaitán A.C., Cabañero-Navalon M.D., Sigona-Giangreco I.A., Pemán J. A Clinical Predictive Model of Candidaemia by Candida Auris in Previously Colonized Critically Ill Patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020;26:1507–1513. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Jong A.W., Hagen F. Attack, Defend and Persist: How the Fungal Pathogen Candida Auris Was Able to Emerge Globally in Healthcare Environments. Volume 184 Springer; Heidelberg, The Netherlands: 2019. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 301304/2017-3/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- AI124797/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- VPPCB-007-FIO-18/Oswaldo Cruz Foundation
- 442317/2019-0/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- 405520/2018-2/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

