Access to Anti-Biofilm Compounds from Endolichenic Fungi Using a Bioguided Networking Screening
- PMID: 36294577
- PMCID: PMC9604612
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8101012
Access to Anti-Biofilm Compounds from Endolichenic Fungi Using a Bioguided Networking Screening
Abstract
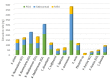
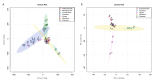
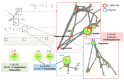
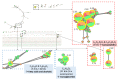
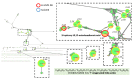
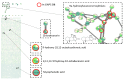
Endolichenic microorganisms represent a new source of bioactive natural compounds. Lichens, resulting from a symbiotic association between algae or cyanobacteria and fungi, constitute an original ecological niche for these microorganisms. Endolichenic fungi inhabiting inside the lichen thallus have been isolated and characterized. By cultivation on three different culture media, endolichenic fungi gave rise to a wide diversity of bioactive metabolites. A total of 38 extracts were screened for their anti-maturation effect on Candida albicans biofilms. The 10 most active ones, inducing at least 50% inhibition, were tested against 24 h preformed biofilms of C. albicans, using a reference strain and clinical isolates. The global molecular network was associated to bioactivity data in order to identify and priorize active natural product families. The MS-targeted isolation led to the identification of new oxygenated fatty acid in Preussia persica endowed with an interesting anti-biofilm activity against C. albicans yeasts.
Keywords: Candida biofilms; endolichenic fungi; fatty acids; metabolomic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
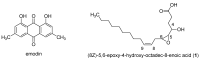
References
-
- Kellogg J.J., Raja H.A. Endolichenic Fungi: A New Source of Rich Bioactive Secondary Metabolites on the Horizon. Phytochem. Rev. 2017;16:271–293. doi: 10.1007/s11101-016-9473-1. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

