Evaluation of Tele-Dentistry and Face-to-Face Appointments during the Provision of Dental Services in Poland
- PMID: 36294779
- PMCID: PMC9605474
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12101640
Evaluation of Tele-Dentistry and Face-to-Face Appointments during the Provision of Dental Services in Poland
Abstract
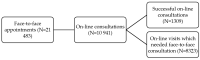
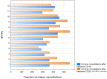
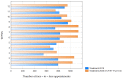
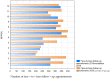
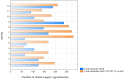
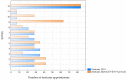
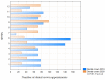
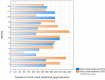
Tele-dentistry is a rapidly growing field, especially in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, remote services are of increasing interest to both patients and dental personnel. They allow for reduced person-to-person contact and thus a reduced risk of transmission of the SARS-CoV2 virus. The COVID-19 pandemic has affected the functioning of all areas of life, including dental treatment. The aim of the study was to assess the possibility of using tele-dentistry for dental services and analyse the attitudes of patients and dentists towards this solution. The period analysed was between March 2019 and February 2021 in five healthcare entities in Cracow in Central Europe. The study's retrospective analysis shows a positive attitude of patients towards tele-dentistry at every stage of treatment, from diagnosis through postoperative care, and a significant reluctance of dentists in the majority of dental specialties towards tele-dentistry. Consequently, a significant percentage of patients were invited to dental offices for a face-to-face appointment during the COVID-19 pandemic. The negative attitude of dental personnel towards tele-dentistry compared with the positive attitude of patients towards tele-dentistry is somewhat worrying in view of the possibility of a further pandemic. At the same time, it provides important information about the need to educate and support dental personnel in tele-dental solutions and improve solutions for the future. Taking into account the potential reduction in dental care costs for patients and countries after the implementation of tele-dentistry solutions, this is an important topic, while current studies do not comprehensively address the attitudes of patients and dental personnel towards tele-dentistry. In other parts of the world, a similar approach to tele-dentistry is used by patients and dentists.
Keywords: COVID-19; dentistry; remote consultation; telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patients' and dentists' perceptions of tele-dentistry at the time of COVID-19. A questionnaire-based study.J Dent. 2021 Oct;113:103782. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2021.103782. Epub 2021 Aug 13. J Dent. 2021. PMID: 34400252 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptions and attitudes of dental practitioners towards impacts of Covid 19 pandemic on clinical dentistry: a cross-sectional study.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Sep 22;22(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02457-y. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 36138429 Free PMC article.
-
Tele-dentistry in COVID-19 era: A conduit for dental care in uncertain times.J Pak Med Assoc. 2024 Apr;74(4 (Supple-4)):S145-S150. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.AKU-9S-22. J Pak Med Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38712423
-
Teledentistry and its applications in paediatric dentistry: A literature review.Pediatr Dent J. 2021 Dec;31(3):203-215. doi: 10.1016/j.pdj.2021.08.003. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Pediatr Dent J. 2021. PMID: 34848924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Revision of dentistry safety guidelines during COVID-19 pandemic].Med Pr. 2021 Nov 19;72(5):561-568. doi: 10.13075/mp.5893.01055. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Med Pr. 2021. PMID: 34491245 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Telemedicine and Digital Tools in Dentistry: Enhancing Diagnosis and Remote Patient Care.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Apr 30;61(5):826. doi: 10.3390/medicina61050826. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40428784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring oral health remotely: ethical considerations when using AI among vulnerable populations.Front Oral Health. 2025 Apr 14;6:1587630. doi: 10.3389/froh.2025.1587630. eCollection 2025. Front Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40297341 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Impact of Teledentistry on Patient Outcomes, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Satisfaction in a Prospective Observational Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Feb 18;16(2):e54424. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54424. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38510897 Free PMC article.
-
eHealth, teledentistry and health workforce challenges: results of a pilot project.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Dec 1;22(1):552. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02603-6. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 36456948 Free PMC article.
-
Acceptance and Willingness-to-Pay for Teledentistry: A Contingent Valuation Study.Int Dent J. 2025 Jun;75(3):1599-1607. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.02.004. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 40138994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marya A., Venugopal A., Karobari M.I., Messina P., Scardina G.A., Subramanian A.K. The Exponential Rise of Teledentistry and Patient-Oriented Protective Measures in Southeast Asian Dental Clinics: Concerns, Benefits, and Challenges. Int. J. Dent. 2021;2021:9963329. doi: 10.1155/2021/9963329. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

