A Review of Digital Health and Biotelemetry: Modern Approaches towards Personalized Medicine and Remote Health Assessment
- PMID: 36294795
- PMCID: PMC9604784
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12101656
A Review of Digital Health and Biotelemetry: Modern Approaches towards Personalized Medicine and Remote Health Assessment
Abstract
With the prevalence of digitalization in all aspects of modern society, health assessment is becoming digital too. Taking advantage of the most recent technological advances and approaching medicine from an interdisciplinary perspective has allowed for important progress in healthcare services. Digital health technologies and biotelemetry devices have been more extensively employed for preventing, detecting, diagnosing, monitoring, and predicting the evolution of various diseases, without requiring wires, invasive procedures, or face-to-face interaction with medical personnel. This paper aims to review the concepts correlated to digital health, classify and describe biotelemetry devices, and present the potential of digitalization for remote health assessment, the transition to personalized medicine, and the streamlining of clinical trials.
Keywords: Internet of Things; artificial intelligence; biotelemetry devices; digital health; medical biotechnology; mobile health; personalized medicine; precision medicine; remote patient monitoring; telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

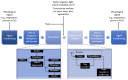
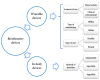
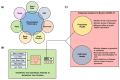
References
-
- Damaj I.W., Iraqi Y., Mouftah H.T. Modern Development Technologies and Health Informatics: Area Transformation and Future Trends. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2020;3:88–94. doi: 10.1109/IOTM.0001.1900077. - DOI
-
- Radzicki V.R., Rajagopal A. Remote Heart Monitoring via Medical Telemetry. Int. Telemetering Conf. Proc. 2019;55:1–10.
-
- Lee B., Ghovanloo M. An Overview of Data Telemetry in Inductively Powered Implantable Biomedical Devices. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019;57:74–80. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1800052. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

