IL-2 and IL-1β Patient Immune Responses Are Critical Factors in SARS-CoV-2 Infection Outcomes
- PMID: 36294868
- PMCID: PMC9605386
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12101729
IL-2 and IL-1β Patient Immune Responses Are Critical Factors in SARS-CoV-2 Infection Outcomes
Abstract
Background: Immune dysregulation has been linked to morbidity and mortality in COVID-19 patients. Understanding the immunology of COVID-19 is critical for developing effective therapies, diagnostics, and prophylactic strategies to control the disease.
Aim: The aim of this study was to correlate cytokine and chemokine serum levels with COVID-19 disease severity and mortality.
Subjects and methods: A total of 60 hospitalized patients from the Tabuk region of Saudi Arabia with confirmed COVID-19 were included in the study. At hospital admission, the IL-1 β, IL-2, IL-8, IL-10, LT-B4, and CCL-2 serum levels were measured. The cytokine levels in COVID-19 patients were compared to the levels in 30 healthy matched control subjects.
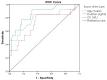
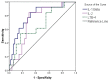
Results: The IL-1 β, IL-2, LTB-4, CCL-2, and IL-8 levels (but not IL-10) were significantly higher in all COVID-19 patients (47 survivors and 13 non-survivors) compared with the levels in the healthy control group. In the non-survivor COVID-19 patients, patients' age, D-dimer, and creatinine kinase were significantly higher, and IL-1 β, IL-2, and IL-8 were significantly lower compared with the levels in the survivors.
Conclusion: Mortality rates in COVID-19 patients are associated with increased age and a failure to mount an effective immune response rather than developing a cytokine storm. These results warrant the personalized treatment of COVID-19 patients based on cytokine profiling.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-1β; IL-2; cytokine storm; immune response; morbidity; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing the Impact of Inflammatory Markers and CT Severity Score on Disease Severity of COVID-19 Patients Admitted to ICU at a Tertiary Hospital.J Assoc Physicians India. 2021 Jun;69(6):11-12. J Assoc Physicians India. 2021. PMID: 34472783
-
Complement Anaphylatoxins and Inflammatory Cytokines as Prognostic Markers for COVID-19 Severity and In-Hospital Mortality.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 1;12:668725. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.668725. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276659 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine Profiles Before and After Immune Modulation in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19.J Clin Immunol. 2021 May;41(4):738-747. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00949-6. Epub 2021 Jan 18. J Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33459964 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of CCR5 signaling to treat COVID-19-associated cytokine storm: Case series of four critically ill patients treated with leronlimab.J Transl Autoimmun. 2021;4:100083. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100083. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33521616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hazards of the Cytokine Storm and Cytokine-Targeted Therapy in Patients With COVID-19: Review.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Aug 13;22(8):e20193. doi: 10.2196/20193. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32707537 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Examination of Feline Coronavirus and Canine Coronavirus Effects on Extracellular Vesicles Acquired from A-72 Canine Fibrosarcoma Cell Line.Vet Sci. 2025 May 15;12(5):477. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12050477. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40431570 Free PMC article.
-
Association between SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia, skewed T cell responses, inflammation, and severity in hospitalized COVID-19 people living with HIV.iScience. 2023 Dec 7;27(1):108673. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108673. eCollection 2024 Jan 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38188525 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-specific T helper cells and cytokine profiles predict intensity and longevity of cellular and humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 booster vaccination.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1423766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1423766. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39267758 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the activity of the immune system in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases and asymptomatic COVID-19.Prz Gastroenterol. 2024;19(1):46-53. doi: 10.5114/pg.2023.124281. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Prz Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38571543 Free PMC article.
-
Early metabolic predictors of type 2 diabetes mellitus in normoglycemic adults: insights from six-year prospective cohort study.Metabolomics. 2025 Aug 11;21(5):104. doi: 10.1007/s11306-025-02295-3. Metabolomics. 2025. PMID: 40790364
References
-
- [(accessed on 20 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/saudi-arabia/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous