Evaluation of Green Silver Nanoparticles Fabricated by Spirulina platensis Phycocyanin as Anticancer and Antimicrobial Agents
- PMID: 36294927
- PMCID: PMC9605328
- DOI: 10.3390/life12101493
Evaluation of Green Silver Nanoparticles Fabricated by Spirulina platensis Phycocyanin as Anticancer and Antimicrobial Agents
Abstract
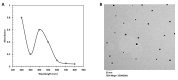
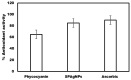
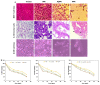
Green nanotechnology has attracted attention worldwide, especially in treating cancer and drug-resistant section 6 microbes. This work aims to investigate the anticancer activity of green silver nanoparticles synthesized by Spirulina platensis phycocyanin (SPAgNPs) on two cancer cell lines: Lung cancer cell line (A-549) and breast cancer cell line (MCF-7), compared to the normal human lung cell line (A138). We also aimed to investigate the bactericidal activity against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC29737, Bacillus cereus ATCC11778, Escherichia coli ATCC8379, and Klebsiella pneumonia, as well as the fungicidal activity against Candida albicans (ATCC6019) and Aspergillus niger. The obtained SPAgNPs were spherical and crystalline with a size of 30 nm and a net charge of -26.32 mV. Furthermore, they were surrounded by active groups responsible for stability. The SPAgNPs scavenged 85% of the DPPH radical with a relative increase of approximately 30% over the extract. The proliferation of cancer cells using the MTT assay clarified that both cancer cells (A-549 and MCF-7) are regularly inhibited as they grow on different concentrations of SPAgNPs. The maximum inhibitory effect of SPAgNPs (50 ppm) reached 90.99 and 89.51% against A-549 and MCF7, respectively. Regarding antimicrobial activity, no inhibition zones occurred in bacterial or fungal strains at low concentrations of SPAgNPs and the aqueous Spirulina platensis extract. However, at high concentrations, inhibition zones, especially SPAgNPs, were more potent for all tested microorganisms than their positive controls, with particular reference to Staphylococcus aureus, since the inhibition zones were 3.2, 3.8, and 4.3 mm, and Bacillus cereus was 2.37 mm when compared to tetracycline (2.33 mm). SPAgNPs have more potent antifungal activity, especially against Aspergillus niger, compared to their positive controls. We concluded that SPAgNPs are powerful agents against oxidative stress and microbial infection.
Keywords: SPAgNPs; Spirulina; anticancer; antimicrobial; cancer; cell lines; phycocyanin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Spirulina platensis extracts and biogenic selenium nanoparticles against selected pathogenic bacteria and fungi.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Feb;29(2):1197-1209. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.046. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35197787 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Functional Silver Nanoparticles and Microparticles with Modifiers and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial, Anticancer, and Antioxidant Activity.J Funct Biomater. 2020 Oct 23;11(4):76. doi: 10.3390/jfb11040076. J Funct Biomater. 2020. PMID: 33113975 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Activity, Apoptotic Induction and Cell Cycle Arrest of New Hydrazonoyl Halides Derivatives.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(9):1141-1149. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666190306123658. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30843494
-
In vitro activity of Spirulina platensis water extract against different Candida species isolated from vulvo-vaginal candidiasis cases.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 30;12(11):e0188567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188567. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29190763 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in delivery methods of Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.Bioengineered. 2022 Jun;13(6):14681-14718. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2100863. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35946342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Selective in vitro Cytotoxicity of Spirulina-Derived Nanoparticles: A Novel Biomimetic Approach to Cancer Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 8;20:4285-4298. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S498865. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40225219 Free PMC article.
-
Development, physicochemical characterization, and antimicrobial evaluation of niosome-loaded oregano essential oil against fish-borne pathogens.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 19;10(5):e26486. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26486. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38463865 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles from Microalgae and Their Biomedical Applications.Mar Drugs. 2023 Jun 7;21(6):352. doi: 10.3390/md21060352. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37367677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutraceutical Features of the Phycobiliprotein C-Phycocyanin: Evidence from Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina).Nutrients. 2024 Jun 3;16(11):1752. doi: 10.3390/nu16111752. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El-Saadony M.T., Sitohy M.Z., Ramadan M.F., Saad A.M. Green nanotechnology for preserving and enriching yogurt with biologically available iron (II) Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021;69:102645. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2021.102645. - DOI
-
- El-Saadony M.T., El-Wafai N.A., El-Fattah H.I.A., Mahgoub S.A. Biosynthesis, optimization and characterization of silver nanoparticles using a soil isolate of Bacillus pseudomycoides MT32 and their antifungal activity against some pathogenic fungi. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2019;7:238–249. doi: 10.17582/journal.aavs/2019/7.4.238.249. - DOI
-
- El-Saadony M.T., Alkhatib F.M., Alzahrani S.O., Shafi M.E., Abdel-Hamid S.E., Taha T.F., Aboelenin S.M., Soliman M.M., Ahmed N.H. Impact of mycogenic zinc nanoparticles on performance, behavior, immune response, and microbial load in Oreochromis niloticus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021;28:4592–4604. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.04.066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Moneim A.-M.E., El-Saadony M.T., Shehata A.M., Saad A.M., Aldhumri S.A., Ouda S.M., Mesalam N.M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Spirulina platensis extracts and biogenic selenium nanoparticles against selected pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022;29:1197–1209. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.046. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- El-Saadony M.T., Saad A.M., Najjar A.A., Alzahrani S.O., Alkhatib F.M., Shafi M.E., Selem E., Desoky E.-S.M., Fouda S.E., El-Tahan A.M. The use of biological selenium nanoparticles to suppress Triticum aestivum L. crown and root rot diseases induced by Fusarium species and improve yield under drought and heat stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021;28:4461–4471. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.04.043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

