The Conserved Family of the Pyridoxal Phosphate-Binding Protein (PLPBP) and Its Cyanobacterial Paradigm PipY
- PMID: 36295057
- PMCID: PMC9605639
- DOI: 10.3390/life12101622
The Conserved Family of the Pyridoxal Phosphate-Binding Protein (PLPBP) and Its Cyanobacterial Paradigm PipY
Abstract
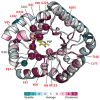
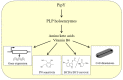
The PLPBP family of pyridoxal phosphate-binding proteins has a high degree of sequence conservation and is represented in all three domains of life. PLPBP members, of which a few representatives have been studied in different contexts, are single-domain proteins with no known enzymatic activity that exhibit the fold type III of PLP-holoenzymes, consisting in an α/β barrel (TIM-barrel), where the PLP cofactor is solvent-exposed. Despite the constant presence of cofactor PLP (a key catalytic element in PLP enzymes), PLPBP family members appear to have purely regulatory functions affecting the homeostasis of vitamin B6 vitamers and amino/keto acids. Perturbation of these metabolites and pleiotropic phenotypes have been reported in bacteria and zebrafish after PLPBP gene inactivation as well as in patients with vitamin B6-dependent epilepsy that results from loss-of-function mutations at the PLPBP. Here, we review information gathered from diverse studies and biological systems, emphasizing the structural and functional conservation of the PLPBP members and discussing the informative nature of model systems and experimental approaches. In this context, the relatively high level of structural and functional characterization of PipY from Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 provides a unique opportunity to investigate the PLPBP roles in the context of a signaling pathway conserved in cyanobacteria.
Keywords: COG0325; PLPBP; PLPHP; PipY; Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942; YggS; cyanobacteria; nitrogen regulation; pyridoxal phosphate; vitamin B6-dependent epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pleiotropic effects of PipX, PipY, or RelQ overexpression on growth, cell size, photosynthesis, and polyphosphate accumulation in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 16;14:1141775. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1141775. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37007489 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the conserved pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-binding protein YggS/PLPBP in vitamin B6 and amino acid homeostasis.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2022 Aug 24;86(9):1183-1191. doi: 10.1093/bbb/zbac113. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35803498 Review.
-
Studies on cyanobacterial protein PipY shed light on structure, potential functions, and vitamin B6 -dependent epilepsy.FEBS Lett. 2017 Oct;591(20):3431-3442. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12841. Epub 2017 Sep 20. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 28914444
-
Mechanism of Pyridoxine 5'-Phosphate Accumulation in Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate-Binding Protein Deficiency.J Bacteriol. 2022 Mar 15;204(3):e0052121. doi: 10.1128/JB.00521-21. Epub 2022 Jan 3. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 34978460 Free PMC article.
-
Disorders affecting vitamin B6 metabolism.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2019 Jul;42(4):629-646. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12060. Epub 2019 Mar 20. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2019. PMID: 30671974 Review.
Cited by
-
The causal effects of 2,821 protein level ratios on non-small cell lung cancer: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 28;14(2):1101-1110. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1523. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40104726 Free PMC article.
-
The ribosome assembly GTPase EngA is involved in redox signaling in cyanobacteria.Front Microbiol. 2023 Aug 10;14:1242616. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1242616. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37637111 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects of PipX, PipY, or RelQ overexpression on growth, cell size, photosynthesis, and polyphosphate accumulation in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 16;14:1141775. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1141775. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37007489 Free PMC article.
-
The Signal Transduction Protein PII Controls the Levels of the Cyanobacterial Protein PipX.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 23;11(10):2379. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11102379. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37894037 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

