Application Value of Systemic Inflammatory Indexes in the Clinical Evaluation of Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)
- PMID: 36295633
- PMCID: PMC9611882
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina58101473
Application Value of Systemic Inflammatory Indexes in the Clinical Evaluation of Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)
Abstract
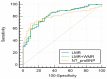
Background: In areas where medical resources are scarce, an economical and convenient way to assess patients’ condition so that treatment plans can be adjusted in a timely manner makes sense. The clinical value of systemic inflammatory indexes (SII) such as neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), albumin-to-gamma-glutamyl-transferase ratio (AGR), white-blood-cell-count-to-mean-platelet-volume ratio (WMR), high-density-lipoprotein-cholesterol-to-C-reactive-protein ratio (HCR), etc. were explored in heart failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) because of their easy availability and clinical value in the diagnosis, therapy and prognosis of cardiovascular diseases. Methods: 189 inpatients (including 48 patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) I in the control group, and 141 patients with NYHA II-IV in the study group) from The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, during the period July 2018 to March 2022, were included by retrieving electronic medical records. Logistic regression analysis, Spearman’s correlation coefficient, operating characteristic curve, etc. were used to analyze the data. Results: In patients with HFpEF, LMR (OR = 0.463, 95% CI 0.348−0.617, p = 0.000), NLR and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) were independent predictors for the presence of HF, and LMR (OR = 2.630, 95% CI 2.016−3.435, p = 0.000), NLR, FAG, MHR, AGR and NT-proBNP were independent predictors for increased NYHA functional classification. There were good correlations (r > 0.4) between LMR (r = −0.667, p = 0.000), NLR, WMR, HCR, NT-proBNP (r = −0.681, p = 0.000) and NYHA functional classification, and LMR (AUC = 0.803, 95% CI 0.729−0.849, p = 0.0001), NLR and NT-proBNP (AUC = 0.805, 95% CI 0.738−0.861, p = 0.0001) had good diagnostic values (AUC > 0.7) for HF in patients with HFpEF. In addition, there were certain correlations between LMR, NT-proBNP and echocardiography indicators of cardiac structural. Conclusions: SII have a potential application value in the clinical evaluation of patients with HFpEF in the follow-up, especially in areas with limited medical resources, as they are more convenient and cost effective. Among different SII, LMR is probably the most promising metric. However, large-scale clinical trials are needed in the future to confirm these findings.
Keywords: HFpEF; NT-proBNP; New York Heart Association (NYHA); lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR); systemic inflammatory indexes (SII).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in the study, or in the authorship and publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Ponikowski P., Voors A.A., Anker S.D., Bueno H., Cleland J.G.F., Coats A.J.S., Falk V., González-Juanatey J.R., Harjola V.P., Jankowska E.A., et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016;37:2129–2200. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dai W., Zhang Z., Zhao S. Baseline levels of serum high sensitivity C reactive protein and lipids in predicting the residual risk of cardiovascular events in Chinese population with stable coronary artery disease: A prospective cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17:273. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0923-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous