Hopomics: Humulus lupulus Brewing Cultivars Classification Based on LC-MS Profiling and Nested Feature Selection
- PMID: 36295846
- PMCID: PMC9609554
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo12100945
Hopomics: Humulus lupulus Brewing Cultivars Classification Based on LC-MS Profiling and Nested Feature Selection
Abstract
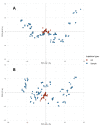
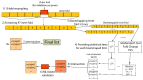
Omics approaches in plant analysis find many different applications, from classification to new bioactive compounds discovery. Metabolomics seems to be one of the most informative ways of describing plants' phenotypes, since commonly used methods such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) could provide a huge amount of information about samples. However, due to high efficiency, many disadvantages arise with the complexity of the experimental design. In the present work, we demonstrate an untargeted metabolomics pipeline with the example of a Humulus lupulus classification task. LC-MS profiling of brewing cultivars samples was carried out as a starting point. Hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA)-based classification in combination with nested feature selection was provided for sample discrimination and marker compounds discovery. Obtained metabolome-based classification showed an expected difference compared to genetic-based classification data. Nine compounds were found to have the biggest classification power during nested feature selection. Using database search and molecular network construction, five of them were identified as known hops bitter compounds.
Keywords: Humulus lupulus; machine learning; metabolomics; untargeted profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kubeš J. Geography of World Hop Production 1990–2019. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2021;80:84–91. doi: 10.1080/03610470.2021.1880754. - DOI
-
- Korpelainen H., Pietiläinen M. Hop (Humulus lupulus L.): Traditional and Present Use, and Future Potential. Econ. Bot. 2021;75:302–322. doi: 10.1007/s12231-021-09528-1. - DOI
-
- Nesvadba V., Charvátová J. New Fine Aroma Varieties of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) Saaz Brilliant, Saaz Comfort, Saaz Shine and Mimosa. Kvas. Prum. 2020;66:320–330. doi: 10.18832/kp2019.66.320. - DOI
-
- van Simaeys K.R., Féchir M., Gallagher A., Stokholm A., Weaver G., Shellhammer T.H. Examining Chemical and Sensory Differences of New American Aroma Hops Grown in the Willamette Valley, Oregon. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2021;79:1–9. doi: 10.1080/03610470.2021.1968271. - DOI
-
- Mongelli A., Rodolfi M., Ganino T., Marieschi M., Dall’Asta C., Bruni R. Italian Hop Germplasm: Characterization of Wild Humulus lupulus L. Genotypes from Northern Italy by Means of Phytochemical, Morphological Traits and Multivariate Data Analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015;70:16–27. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.02.036. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

