Schistosomiasis Mansoni-Recruited Eosinophils: An Overview in the Granuloma Context
- PMID: 36296298
- PMCID: PMC9607553
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10102022
Schistosomiasis Mansoni-Recruited Eosinophils: An Overview in the Granuloma Context
Abstract
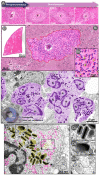
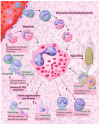
Eosinophils are remarkably recruited during schistosomiasis mansoni, one of the most common parasitic diseases worldwide. These cells actively migrate and accumulate at sites of granulomatous inflammation termed granulomas, the main pathological feature of this disease. Eosinophils colonize granulomas as a robust cell population and establish complex interactions with other immune cells and with the granuloma microenvironment. Eosinophils are the most abundant cells in granulomas induced by Schistosoma mansoni infection, but their functions during this disease remain unclear and even controversial. Here, we explore the current information on eosinophils as components of Schistosoma mansoni granulomas in both humans and natural and experimental models and their potential significance as central cells triggered by this infection.
Keywords: Schistosoma mansoni; eosinophil degranulation; eosinophils; granuloma; hepatic granuloma; histopathology; inflammation; schistosomiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gazzinelli G., Lambertucci J.R., Katz N., Rocha R.S., Lima M.S., Colley D.G. Immune responses during human Schistosomiasis mansoni. XI. Immunologic status of patients with acute infections and after treatment. J. Immunol. 1985;135:2121–2127. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

