Alzheimer's Disease as a Major Public Health Concern: Role of Dietary Saponins in Mitigating Neurodegenerative Disorders and Their Underlying Mechanisms
- PMID: 36296397
- PMCID: PMC9608803
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27206804
Alzheimer's Disease as a Major Public Health Concern: Role of Dietary Saponins in Mitigating Neurodegenerative Disorders and Their Underlying Mechanisms
Abstract
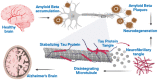
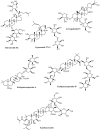
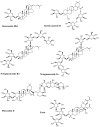
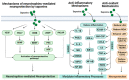
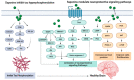
Saponins are triterpenoid or steroidal glycosides and are an important group of naturally occurring compounds of plant origin. They exhibit diverse pharmacological potentials including radical scavenging, as well as neuroprotective, anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory activities, owing to their diverse chemical scaffolds. Saponins consist of an aglycone part (non-sugar) and a glycone part (sugar) and have at least one glycosidic (C-O sugar bond) linkage present between the glycone and aglycone mostly at C-3. On the basis of the aglycone part, saponins are classified into triterpenoid glycosides, steroid glycosides and alkaloid glycosides. Saponins exhibit neuroprotective activities against various disorders of the central nervous system (CNS) including stroke, Alzheimer's disease (AD), Huntington's disease (HD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). They mediate their therapeutic effects by modulation of various pathological targets. This study highlights various neuroprotective mechanisms of saponins including free radical scavenging, modulation of neuroprotective signaling pathways, activation of neurotrophic factors, modulation of neurotransmitters, inhibition of BACE1 enzyme and tau hyper-phosphorylation. The study concludes that saponins have considerable efficacy against various pathological targets of neurological disorders, especially AD, and might be an important source of leads against neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; neurodegenerative disorders; neurotrophins; saponins; signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liu Z., Zhang A., Sun H., Han Y., Kong L., Wang X. Two decades of new drug discovery and development for Alzheimer’s disease. RSC Adv. 2017;7:6046–6058. doi: 10.1039/C6RA26737H. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

