Supplementation of SDF1 during Pig Oocyte In Vitro Maturation Improves Subsequent Embryo Development
- PMID: 36296422
- PMCID: PMC9609306
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27206830
Supplementation of SDF1 during Pig Oocyte In Vitro Maturation Improves Subsequent Embryo Development
Abstract
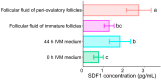
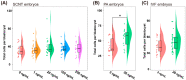
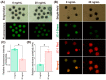
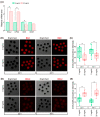
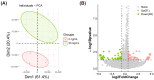
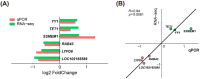
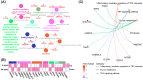
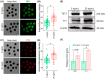
The quality of in vitro matured oocytes is inferior to that of in vivo matured oocytes, which translates to low developmental capacity of embryos derived from in vitro matured oocytes. The developmental potential of in vitro matured oocytes is usually impaired due to oxidative stress. Stromal cell-derived factor-l (SDF1) can reduce oxidative stress and inhibit apoptosis. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of SDF1 supplementation during pig oocyte in vitro maturation (IVM) on subsequent embryo development, and to explore the acting mechanisms of SDF1 in pig oocytes. We found that the IVM medium containing 20 ng/mL SDF1 improved the maturation rate of pig oocytes, as well as the cleavage rate and blastocyst rate of embryos generated by somatic cell nuclear transfer, in vitro fertilization, and parthenogenesis. Supplementation of 20 ng/mL SDF1 during IVM decreased the ROS level, increased the mitochondrial membrane potential, and altered the expression of apoptosis-related genes in the pig oocytes. The porcine oocyte transcriptomic data showed that SDF1 addition during IVM altered the expression of genes enriched in the purine metabolism and TNF signaling pathways. SDF1 supplementation during pig oocyte IVM also upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of YY1 and TET1, two critical factors for oocyte development. In conclusion, supplementation of SDF1 during pig oocyte IVM reduces oxidative stress, changes expression of genes involved in regulating apoptosis and oocyte growth, and enhances the ability of in vitro matured pig oocytes to support subsequent embryo development. Our findings provide a theoretical basis and a new method for improving the developmental potential of pig in vitro matured oocytes.
Keywords: IVM; SDF1; embryo development; oocyte quality; pig.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare they have no conflict of interest that could inappropriately influence or be perceived to influence the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Docosahexaenoic acid supplementation during porcine oocyte in vitro maturation improves oocyte quality and embryonic development by enhancing the homeostasis of energy metabolism.Theriogenology. 2024 Oct 1;227:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2024.07.002. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Theriogenology. 2024. PMID: 39013287
-
A pre-in vitro maturation medium containing cumulus oocyte complex ligand-receptor signaling molecules maintains meiotic arrest, supports the cumulus oocyte complex and improves oocyte developmental competence.Mol Hum Reprod. 2017 Sep 1;23(9):594-606. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gax032. Mol Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28586460
-
Effect of alanine supplementation during in vitro maturation on oocyte maturation and embryonic development after parthenogenesis and somatic cell nuclear transfer in pigs.Theriogenology. 2019 Mar 15;127:80-87. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Theriogenology. 2019. PMID: 30677595
-
Mechanisms of action of non-enzymatic antioxidants to control oxidative stress during in vitro follicle growth, oocyte maturation, and embryo development.Anim Reprod Sci. 2023 Feb;249:107186. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2022.107186. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Anim Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 36638648 Review.
-
The Effect of CoQ10 supplementation on ART treatment and oocyte quality in older women.Hum Fertil (Camb). 2023 Dec;26(6):1544-1552. doi: 10.1080/14647273.2023.2194554. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Hum Fertil (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37102567 Review.
Cited by
-
Beneficial Effects of Catalpol Supplementation during In Vitro Maturation of Porcine Cumulus-Oocyte Complexes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 5;12(6):1222. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061222. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371952 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation with Eupatilin during In Vitro Maturation Improves Porcine Oocyte Developmental Competence by Regulating Oxidative Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jan 30;14(3):449. doi: 10.3390/ani14030449. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38338092 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of melatonin on in vitro oocyte maturation and embryo development in pigs.Vet World. 2025 May;18(5):1234-1241. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2025.1234-1241. Epub 2025 May 21. Vet World. 2025. PMID: 40584118 Free PMC article.
-
Progesterone and Androstenedione Are Important Follicular Fluid Factors Regulating Porcine Oocyte Maturation Quality.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 30;13(11):1811. doi: 10.3390/ani13111811. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37889685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao H., Xie S., Zhang N., Ao Z., Wu X., Yang L., Shi J., Mai R., Zheng E., Cai G., et al. Source and Follicular Fluid Treatment During the In Vitro Maturation of Recipient Oocytes Affects the Development of Cloned Pig Embryo. Cell. Reprogram. 2020;22:71–81. doi: 10.1089/cell.2019.0091. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019B1515210027/Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province, China
- 2019BT02N630/Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province, China
- 2020A1414010045/Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province, China
- 2021020601/Department of Science and Technology of Yunfu City, Guangdong Province, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

