Heparin-Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications
- PMID: 36296711
- PMCID: PMC9611043
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27207116
Heparin-Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications
Abstract
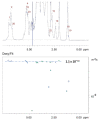
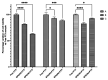
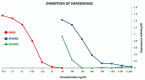
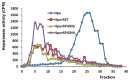
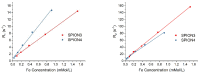
In this study, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) were engineered with an organic coating composed of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) and bovine serum albumin (BSA), providing heparin-based nanoparticle systems (LMWH@SPIONs). The purpose was to merge the properties of the heparin skeleton and an inorganic core to build up a targeted theranostic nanosystem, which was eventually enhanced by loading a chemotherapeutic agent. Iron oxide cores were prepared via the co-precipitation of iron salts in an alkaline environment and oleic acid (OA) capping. Dopamine (DA) was covalently linked to BSA and LMWH by amide linkages via carbodiimide coupling. The following ligand exchange reaction between the DA-BSA/DA-LMWH and OA was conducted in a biphasic system composed of water and hexane, affording LMWH@SPIONs stabilized in water by polystyrene sulfonate (PSS). Their size and morphology were investigated via dynamic light scattering (DLS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), respectively. The LMWH@SPIONs' cytotoxicity was tested, showing marginal or no toxicity for samples prepared with PSS at concentrations of 50 µg/mL. Their inhibitory activity on the heparanase enzyme was measured, showing an effective inhibition at concentrations comparable to G4000 (N-desulfo-N-acetyl heparin, a non-anticoagulant and antiheparanase heparin derivative; Roneparstat). The LMWH@SPION encapsulation of paclitaxel (PTX) enhanced the antitumor effect of this chemotherapeutic on breast cancer cells, likely due to an improved internalization of the nanoformulated drug with respect to the free molecule. Lastly, time-domain NMR (TD-NMR) experiments were conducted on LMWH@SPIONs obtaining relaxivity values within the same order of magnitude as currently used commercial contrast agents.
Keywords: dopamine; heparanase; heparin; metastasis; paclitaxel; superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION); theranostic; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Albumin and Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded with Paclitaxel for Biomedical Applications.Molecules. 2017 Jun 22;22(7):1030. doi: 10.3390/molecules22071030. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28640222 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization, Characterization and in vivo Evaluation of Paclitaxel-Loaded Folate-Conjugated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 19;16:2283-2295. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S287434. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33776433 Free PMC article.
-
7-nm Mn0.5 Zn0.5Fe2O4 superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPION): a high-performance theranostic for MRI and hyperthermia applications.Theranostics. 2025 Feb 10;15(7):2883-2902. doi: 10.7150/thno.103503. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40083938 Free PMC article.
-
Surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Oct 18;44(10):853-62. doi: 10.1021/ar2000277. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21528865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) for in vitro and in vivo cancer nanotheranostics.Int J Pharm. 2015 Dec 30;496(2):191-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.10.058. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26520409 Review.
Cited by
-
Block Copolymer-Assisted Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Effective Removal of Congo Red.Molecules. 2023 Feb 17;28(4):1914. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041914. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838902 Free PMC article.
-
Upcycling Eggshell Matrix for Sustainable Production of Glycosaminoglycans.Biopolymers. 2025 Sep;116(5):e70040. doi: 10.1002/bip.70040. Biopolymers. 2025. PMID: 40690197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Dentistry in Oral Cancer Treatment Using Biosynthesis Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: A Systematic Review.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Sep 11;16:1231-1245. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S477791. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 39282609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coene A., Leliaert J. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Theranostic Applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2022;131:160902. doi: 10.1063/5.0085202. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

