Phytochemical Composition and In Vitro Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Anticancer, and Enzyme-Inhibitory Activities of Artemisia nilagirica (C.B. Clarke) Pamp
- PMID: 36296712
- PMCID: PMC9611367
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27207119
Phytochemical Composition and In Vitro Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Anticancer, and Enzyme-Inhibitory Activities of Artemisia nilagirica (C.B. Clarke) Pamp
Abstract
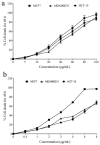
Plants have been employed in therapeutic applications against various infectious and chronic diseases from ancient times. Various traditional medicines and folk systems have utilized numerous plants and plant products, which act as sources of drug candidates for modern medicine. Artemisia is a genus of the Asteraceae family with more than 500 species; however, many of these species are less explored for their biological efficacy, and several others are lacking scientific explanations for their uses. Artemisia nilagirica is a plant that is widely found in the Western Ghats, Kerala, India and is a prominent member of the genus. In the current study, the phytochemical composition and the antioxidant, enzyme-inhibitory, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities were examined. The results indicated that the ethanol extract of A. nilagirica indicated in vitro DPPH scavenging (23.12 ± 1.28 µg/mL), ABTS scavenging (27.44 ± 1.88 µg/mL), H2O2 scavenging (12.92 ± 1.05 µg/mL), and FRAP (5.42 ± 0.19 µg/mL). The anti-inflammatory effect was also noticed in the Raw 264.7 macrophages, where pretreatment with the extract reduced the LPS-stimulated production of cytokines (p < 0.05). A. nilagirica was also efficient in inhibiting the activities of α-amylase (38.42 ± 2.71 µg/mL), α-glucosidase (55.31 ± 2.16 µg/mL), aldose reductase (17.42 ± 0.87 µg/mL), and sorbitol dehydrogenase (29.57 ± 1.46 µg/mL). It also induced significant inhibition of proliferation in breast (MCF7 IC50 = 41.79 ± 1.07, MDAMB231 IC50 = 55.37 ± 2.11µg/mL) and colon (49.57 ± 1.46 µg/mL) cancer cells. The results of the phytochemical screening indicated a higher level of polyphenols and flavonoids in the extract and the LCMS analysis revealed the presence of various bioactive constituents including artemisinin.
Keywords: Artemisia nilagirica; Asteraceae; anti-inflammatory activity; anticancer activity; antioxidant; phytochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytochemical Composition and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Humboldtia sanjappae Sasidh. & Sujanapal, an Endemic Medicinal Plant to the Western Ghats.Molecules. 2023 Sep 29;28(19):6875. doi: 10.3390/molecules28196875. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37836717 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Pharmacological Potential of Miliusa nilagirica Bedd. Leaves Using In Vitro Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Assays.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Nov;195(11):6790-6808. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04396-y. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36930407
-
Phytochemical Characterization, Anti-Oxidant, Anti-Enzymatic and Cytotoxic Effects of Artemisia verlotiorum Lamotte Extracts: A New Source of Bioactive Agents.Molecules. 2022 Sep 10;27(18):5886. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185886. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144622 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Use, Phytochemical Profiles and Pharmacological Properties of Artemisia Genus from Central Asia.Molecules. 2022 Aug 11;27(16):5128. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165128. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicology of the Genus Artemisia L. (Asteraceae): A High-value Medicinal Plant.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(4):301-342. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666230914104141. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37711006 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatoprotective and cardioprotective effect of Artemisia nilagirica leaf extract on E. coli challenged broiler chicken.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 10;10(4):e25709. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25709. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38390080 Free PMC article.
-
GC-MS profiling and computational analysis of Balanites aegyptiaca phytoconstituents for antidiabetic activity: insights from network pharmacology and molecular docking.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 6. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04187-8. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40328910
-
Potential Antiproliferative and Antimetastatic Effects of Artemisia eriantha: An In Vitro Study Focused on Hepatocarcinoma Cells.Biology (Basel). 2024 Nov 28;13(12):985. doi: 10.3390/biology13120985. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behera N.K., Mahalakshmi G.S. A cloud based knowledge discovery framework, for medicinal plants from PubMed literature. Inform. Med. Unlocked. 2019;16:100105. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2018.04.006. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous