Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum OLL2712 on Memory Function in Older Adults with Declining Memory: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36296983
- PMCID: PMC9610166
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14204300
Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum OLL2712 on Memory Function in Older Adults with Declining Memory: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
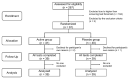
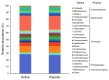
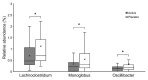
The use of probiotics is expected to be an intervention in neurodegenerative conditions that cause dementia owing to their ability to modulate neuroinflammatory responses via the microbiome-gut-brain axis. Therefore, we selected Lactiplantibacillus plantarum OLL2712 (OLL2712), the optimal anti-inflammatory lactic acid bacteria strain with high IL-10-inducing activity in immune cells, and aimed to verify its protective effects on memory function in older adults. A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was performed with older adults over the age of 65 years with declining memory. The participants consumed either powder containing heat-treated OLL2712 cells or placebo. Memory function was assessed using a computer-assisted cognitive test, Cognitrax. Daily dietary nutrient intake was assessed using the Brief-type Self-administered Diet History Questionnaire (BDHQ). The composition of the gut microbiota was analyzed by fecal DNA extraction and 16S rDNA sequencing. Data from 78 participants who completed the entire procedure were analyzed, and significant improvements in composite memory and visual memory scores were observed in the active group, after accounting for the effect of daily nutritional intake (p = 0.044 and p = 0.021, respectively). In addition, the active group had a lower abundance ratio of Lachnoclostridium, Monoglobus, and Oscillibacter genera, which have been reported to be involved in inflammation. The present study suggests that OLL2712 ingestion has protective effects against memory function decline in older adults.
Keywords: Lactiplantibacillus; aging; gut microbiota; memory; mild cognitive impairment; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
T.T. and T.S. are employees of Meiji Co., Ltd. The other authors, K.S., E.O., S.A., I.S., N.I., S.K. and T.H. report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Dementia. [(accessed on 22 June 2020)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia.
-
- McKhann G.M., Knopman D.S., Chertkow H., Hyman B.T., Jack C.R., Jr., Kawas C.H., Klunk W.E., Koroshetz W.J., Manly J.J., Mayeux R., et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011;7:263–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

