Phenolic Acids as Antidepressant Agents
- PMID: 36296993
- PMCID: PMC9610055
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14204309
Phenolic Acids as Antidepressant Agents
Abstract
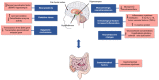
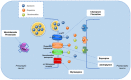
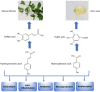
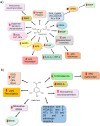
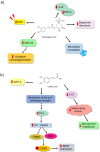
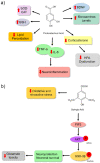
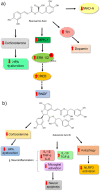
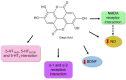
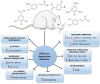
Depression is a psychiatric disorder affecting the lives of patients and their families worldwide. It is an important pathophysiology; however, the molecular pathways involved are not well understood. Pharmacological treatment may promote side effects or be ineffective. Consequently, efforts have been made to understand the molecular pathways in depressive patients and prevent their symptoms. In this context, animal models have suggested phytochemicals from medicinal plants, especially phenolic acids, as alternative treatments. These bioactive molecules are known for their antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities. They occur in some fruits, vegetables, and herbal plants. This review focused on phenolic acids and extracts from medicinal plants and their effects on depressive symptoms, as well as the molecular interactions and pathways implicated in these effects. Results from preclinical trials indicate the potential of phenolic acids to reduce depressive-like behaviour by regulating factors associated with oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, autophagy, and deregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, stimulating monoaminergic neurotransmission and neurogenesis, and modulating intestinal microbiota.
Keywords: antiinflammatory; antioxidants; behaviour; depression; medicinal plants; phenolic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates. 2017. [(accessed on 25 March 2020)]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/254610.
-
- Vismari L., Alves G.J., Palermo-Neto J. Depression, antidepressants and imune system: A new look to an old problem. Rev. Psiquiatr. Clín. 2008;35:196–204. doi: 10.1590/S0101-60832008000500004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

