Immunoproteomic Analysis of Trichinella britovi Proteins Recognized by IgG Antibodies from Meat Juice of Carnivores Naturally Infected with T. britovi
- PMID: 36297212
- PMCID: PMC9612144
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11101155
Immunoproteomic Analysis of Trichinella britovi Proteins Recognized by IgG Antibodies from Meat Juice of Carnivores Naturally Infected with T. britovi
Abstract
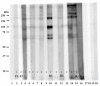
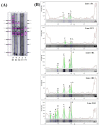
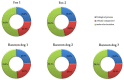
Infection with Trichinella nematodes elicits non-specific and specific immune responses; these depend on the dose of infection, the nematode, and the host species. Few studies have examined the presence of specific antibodies against Trichinella spp. in the meat juice of wild animals. The aims of the study were to determine the prevalence of antibodies against Trichinella spp. in meat juice and to identify the specific proteins reacting with the meat juice from free-living carnivores naturally infected with the parasite. Meat juice samples were taken from foxes, badgers, raccoon dogs, and martens and tested with indirect ELISA. Antibodies against Trichinella spp. were detected in 10% of foxes and 46% of raccoon dogs. The ELISA results were confirmed by immunoblot, which revealed different protein patterns in meat juice from red foxes, raccoon dogs, and badgers. The most frequently observed bands were sent for further analysis by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for the detection of Trichinella britovi immunogenic proteins. The results confirm the presence of proteins such as serine protease and heat shock proteins associated with Trichinella infection. These findings provide that meat juice is a useful matrix for proteomic analysis.
Keywords: Trichinella britovi; antibodies; meat juice immunology; wildlife.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunoproteomic analysis of Trichinella spiralis and Trichinella britovi excretory-secretory muscle larvae proteins recognized by sera from humans infected with Trichinella.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 5;15(11):e0241918. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241918. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33152047 Free PMC article.
-
Trichinella britovi muscle larvae and adult worms: stage-specific and common antigens detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis-based immunoblotting.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Nov 12;11(1):584. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3177-x. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 30419953 Free PMC article.
-
Trichinella spp. biomass has increased in raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Estonia.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Dec 16;10(1):609. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2571-0. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 29246168 Free PMC article.
-
The occurrence and muscle distribution of Trichinella britovi in raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in wildlife in the Głęboki Bród Forest District, Poland.Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2019 May 11;9:149-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2019.05.003. eCollection 2019 Aug. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2019. PMID: 31193289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trichinella britovi in the jackal Canis aureus from south-west Iran.J Helminthol. 2014 Dec;88(4):385-8. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X1300028X. Epub 2013 May 9. J Helminthol. 2014. PMID: 23656910 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Response of the Host and Vaccine Development.Pathogens. 2023 Apr 24;12(5):637. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12050637. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37242307 Free PMC article.
-
Wildlife parasitology: sample collection and processing, diagnostic constraints, and methodological challenges in terrestrial carnivores.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Mar 13;17(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06226-4. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38481271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The First Identification of Trichinella britovi in the Raccoon Dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Romania.Pathogens. 2023 Sep 5;12(9):1132. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12091132. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37764940 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

