Strategizing Drug Therapies in Pulmonary Hypertension for Improved Outcomes
- PMID: 36297354
- PMCID: PMC9609426
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15101242
Strategizing Drug Therapies in Pulmonary Hypertension for Improved Outcomes
Abstract
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is characterized by a resting mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) of 20 mmHg or more and is a disease of multiple etiologies. Of the various types of PH, pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is characterized by elevated resistance in the pulmonary arterial tree. It is a rare but deadly disease characterized by vascular remodeling of the distal pulmonary arteries. This paper focuses on PAH diagnosis and management including current and future treatment options. Over the last 15 years, our understanding of this progressive disease has expanded from the concept of vasoconstrictive/vasodilatory mismatch in the pulmonary arterioles to now a better appreciation of the role of genetic determinants, numerous cell signaling pathways, cell proliferation and apoptosis, fibrosis, thrombosis, and metabolic abnormalities. While knowledge of its pathophysiology has expanded, the majority of the treatments available today still modulate the same three vasodilatory pathways that have been targeted for over 30 years (endothelin, nitric oxide, and prostacyclin). While modifying these pathways may help improve symptoms and quality of life, none of these directly modify the underlying disease pathogenesis. However, there are now studies ongoing with new drugs that can prevent or reverse these underlying causes of PAH. This review discusses the evidence base for the current treatment algorithms for PAH, as well as discusses novel therapies in development.
Keywords: basic research; drug targets; mechanisms of drug action; pulmonary hypertension; reverse translational research; therapeutic approaches; translational research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

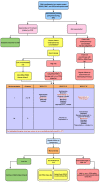


References
-
- Brown L.M., Chen H., Halpern S., Taichman D., McGoon M.D., Farber H.W., Frost A.E., Liou T.G., Turner M., Feldkircher K., et al. Delay in Recognition of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Factors Identified from the REVEAL Registry. Chest. 2011;140:19–26. doi: 10.1378/chest.10-1166. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Humbert M., Kovacs G., Hoeper M.M., Badagliacca R., Berger R.M.F., Brida M., Carlsen J., Coats A.J.S., Escribano-Subias P., Ferrari P., et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension: Developed by the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Endorsed by the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) and the European Reference Network on Rare Respiratory Diseases (ERN-LUNG) Eur. Heart J. 2022:ehac237. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac237. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

