An Investigation of O-Demethyl Tramadol/Tramadol Ratio for Cytochrome P450 2D6 Phenotyping: The CYTRAM Study
- PMID: 36297612
- PMCID: PMC9611900
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102177
An Investigation of O-Demethyl Tramadol/Tramadol Ratio for Cytochrome P450 2D6 Phenotyping: The CYTRAM Study
Abstract
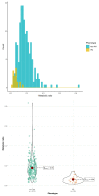
Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) gene polymorphisms influence the exposure to tramadol (T) and its pharmacologically active metabolite, O-demethyl tramadol (O-dT). Tramadol has been considered as a candidate probe drug for CYP2D6 phenotyping. The objective of the CYTRAM study was to investigate the value of plasma O-dT/T ratio for CYP2D6 phenotyping. European adult patients who received IV tramadol after surgery were included. CYP2D6 genotyping was performed and subjects were classified as extensive (EM), intermediate (IM), poor (PM), or ultra-rapid (UM) CYP2D6 metabolizers. Plasma concentrations of tramadol and O-dT were determined at 24 h and 48 h. The relationship between O-dT/T ratio and CYP2D6 phenotype was examined in both a learning and a validation group. Genotype data were obtained in 301 patients, including 23 PM (8%), 117 IM (39%), 154 EM (51%), and 7 UM (2%). Tramadol trough concentrations at 24 h were available in 297 patients. Mean value of O-dT/T ratio was significantly lower in PM than in non-PM individuals (0.061 ± 0.031 versus 0.178 ± 0.09, p < 0.01). However, large overlap was observed in the distributions of O-dT/T ratio between groups. Statistical models based on O-dT/T ratio failed to identify CYP2D6 phenotype with acceptable sensitivity and specificity. Those results suggest that tramadol is not an adequate probe drug for CYP2D6 phenotyping.
Keywords: CYP2D6; pharmacogenetics; pharmacogenomics; tramadol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tramadol as a new probe for cytochrome P450 2D6 phenotyping: a population study.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Jun;77(6):458-67. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2005.01.014. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15961977
-
Impact of CYP2D6 genetic polymorphism on tramadol pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.Mol Diagn Ther. 2007;11(3):171-81. doi: 10.1007/BF03256239. Mol Diagn Ther. 2007. PMID: 17570739
-
Tramadol Therapy and CYP2D6 Genotype.2015 Sep 10 [updated 2025 Jan 17]. In: Pratt VM, Scott SA, Pirmohamed M, Esquivel B, Kattman BL, Malheiro AJ, editors. Medical Genetics Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012–. 2015 Sep 10 [updated 2025 Jan 17]. In: Pratt VM, Scott SA, Pirmohamed M, Esquivel B, Kattman BL, Malheiro AJ, editors. Medical Genetics Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012–. PMID: 28520365 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Concentrations of tramadol and O-desmethyltramadol enantiomers in different CYP2D6 genotypes.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Jul;82(1):41-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.clpt.6100152. Epub 2007 Mar 14. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17361124 Clinical Trial.
-
Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 2D6 and its clinical significance: Part I.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009;48(11):689-723. doi: 10.2165/11318030-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009. PMID: 19817501 Review.
Cited by
-
Crizotinib inhibits the metabolism of tramadol by non-competitive suppressing the activities of CYP2D1 and CYP3A2.PeerJ. 2024 May 30;12:e17446. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17446. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38827306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The Pharmacogenomics Knowledgebase (PharmGKB) Very Important Pharmacogene: CYP2D6. [(accessed on 27 April 2022)]. Available online: https://www.pharmgkb.org/vip/PA166170264.
-
- Caudle K.E., Sangkuhl K., Whirl-Carrillo M., Swen J.J., Haidar C.E., Klein T.E., Gammal R.S., Relling M.V., Scott S.A., Hertz D.L., et al. Standardizing CYP2D6 Genotype to Phenotype Translation: Consensus Recommendations from the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium and Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020;13:116–124. doi: 10.1111/cts.12692. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

