The Influence of Syringic Acid and Erucic Acid on the Antioxidant Properties of Natural Rubber: Experimental and Molecular Simulation Investigations
- PMID: 36297834
- PMCID: PMC9610587
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14204254
The Influence of Syringic Acid and Erucic Acid on the Antioxidant Properties of Natural Rubber: Experimental and Molecular Simulation Investigations
Abstract
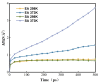
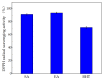
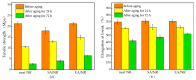
In this work, the influence of syringic acid (SA) and erucic acid (EA) on the oxidation resistance of natural rubber (NR) was investigated by combining experimental and computational methods. The antioxidant activities of SA and EA were predicted by calculating the enthalpy of bond dissociation (BDE), the anti-migration ability of antioxidants (AOs) in the rubber matrix by calculating the mean square displacement (MSD), and the effect of antioxidants on oxygen barrier properties of rubber materials by calculating the permeability coefficient (P). The predicted result is that EA has a better comprehensive performance than SA. The DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) test and mechanical properties test demonstrated the results predicted by the simulations. Both SA and EA can protect natural rubber, while EA has a better comprehensive effect.
Keywords: antioxidative activity; molecular dynamics simulation; natural phenolic antioxidants; natural rubber; quantum mechanics simulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




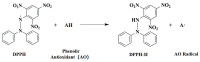
Similar articles
-
Effects of natural antioxidants on the oxidative stability of Eucommia ulmoides seed oil: Experimental and molecular simulation investigations.Food Chem. 2022 Jul 30;383:132640. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132640. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35413767
-
A Study on the Aging Mechanism and Anti-Aging Properties of Nitrile Butadiene Rubber: Experimental Characterization and Molecular Simulation.Polymers (Basel). 2025 May 23;17(11):1446. doi: 10.3390/polym17111446. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508688 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the anti-aging mechanisms of natural phenolic antioxidants in natural rubber composites using a screening strategy based on molecular simulation.RSC Adv. 2020 Jun 4;10(36):21318-21327. doi: 10.1039/d0ra03425h. eCollection 2020 Jun 2. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35518775 Free PMC article.
-
Syringic acid (SA) ‒ A Review of Its Occurrence, Biosynthesis, Pharmacological and Industrial Importance.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Dec;108:547-557. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.069. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30243088 Review.
-
A comprehensive review on the recent advancements in natural rubber nanocomposites.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Jan 1;194:819-842. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.134. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 34838576 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiaging Potential of Lipophilic Extracts of Caulerpa prolifera.Mar Drugs. 2025 Feb 14;23(2):83. doi: 10.3390/md23020083. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39997207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhong B., Dong H., Luo Y., Zhang D., Jia Z., Jia D., Liu F. Simultaneous reduction and functionalization of graphene oxide via antioxidant for highly aging resistant and thermal conductive elastomer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017;151:156–163. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.08.019. - DOI
-
- Matchawet S., Kaesaman A. Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Conductive Carbon Black Filled Epoxidized Natural Rubber. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014;884:255–258. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.844.255. - DOI
-
- Seentrakoon B., Junhasavasdikul B., Chavasiri W. Enhanced UV-protection and antibacterial properties of natural rubber/rutile-TiO2 nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. 2013;98:566–578. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.11.018. - DOI
-
- Palosuo T., Makinen-Kiljunen H., Alenius H., Reunala E., Yip K., Turjanmaa K. Measurement of natural rubber latex allergen levels in medical gloves by allergen-specific IgE-ELISA inhibition, RAST inhibition, and skin prick test. Allergy. 2010;53:59–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1998.tb03774.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barrera C.S., Cornis K. Novel Mineral and Organic Materials from AgroIndustrial Residues as Fillers for Natural Rubber. Polym. Environ. 2015;23:437–448. doi: 10.1007/s10924-015-0737-4. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 52173057/Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZR2020LFG001/Joint Funds of the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China
- KF2020001/Open Fund Project of Key Laboratory of Rubber-Plastics, Ministry of Education/Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Rubber-Plastics
- 2021GGJS110/Training Program for Young Backbone Teachers in Henan Colleges and Universities
- K2022MS005/the Natural Science Foundation of Zhongyuan University of Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

