An Adaptive Task-Related Component Analysis Method for SSVEP Recognition
- PMID: 36298064
- PMCID: PMC9607074
- DOI: 10.3390/s22207715
An Adaptive Task-Related Component Analysis Method for SSVEP Recognition
Abstract
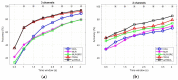
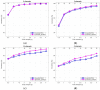
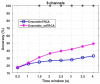
Steady-State Visual Evoked Potential (SSVEP) recognition methods use a subject's calibration data to differentiate between brain responses, hence, providing the SSVEP-based brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) with high performance. However, they require sufficient calibration EEG trials to achieve that. This study develops a new method to learn from limited calibration EEG trials, and it proposes and evaluates a novel adaptive data-driven spatial filtering approach for enhancing SSVEP detection. The spatial filter learned from each stimulus utilizes temporal information from the corresponding EEG trials. To introduce the temporal information into the overall procedure, a multitask learning approach, based on the Bayesian framework, is adopted. The performance of the proposed method was evaluated into two publicly available benchmark datasets, and the results demonstrated that our method outperformed competing methods by a significant margin.
Keywords: EEG; brain–computer interfaces; multitask learning; spatial filtering; steady-state visual evoked potentials; task-related component analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Improving the Performance of Individually Calibrated SSVEP-BCI by Task- Discriminant Component Analysis.IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2021;29:1998-2007. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3114340. Epub 2021 Oct 1. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2021. PMID: 34543200
-
Almost free of calibration for SSVEP-based brain-computer interfaces.J Neural Eng. 2023 Nov 22;20(6). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad0b8f. J Neural Eng. 2023. PMID: 37948768
-
Inter- and Intra-Subject Transfer Reduces Calibration Effort for High-Speed SSVEP-Based BCIs.IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2020 Oct;28(10):2123-2135. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3019276. Epub 2020 Aug 25. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2020. PMID: 32841119
-
An Idle-State Detection Algorithm for SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces Using a Maximum Evoked Response Spatial Filter.Int J Neural Syst. 2015 Nov;25(7):1550030. doi: 10.1142/S0129065715500306. Epub 2015 Jul 5. Int J Neural Syst. 2015. PMID: 26246229
-
Data Augmentation of SSVEPs Using Source Aliasing Matrix Estimation for Brain-Computer Interfaces.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023 Jun;70(6):1775-1785. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2022.3227036. Epub 2023 May 19. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 37015587
Cited by
-
Dataset Evaluation Method and Application for Performance Testing of SSVEP-BCI Decoding Algorithm.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 11;23(14):6310. doi: 10.3390/s23146310. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514603 Free PMC article.
-
A novel hybrid method based on task-related component and canonical correlation analyses (H-TRCCA) for enhancing SSVEP recognition.Front Neurosci. 2025 Apr 25;19:1544452. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1544452. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40352906 Free PMC article.
-
Human Recognition Using Deep Neural Networks and Spatial Patterns of SSVEP Signals.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 22;23(5):2425. doi: 10.3390/s23052425. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904629 Free PMC article.
-
A Sparse Representation Classification Scheme for the Recognition of Affective and Cognitive Brain Processes in Neuromarketing.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 23;23(5):2480. doi: 10.3390/s23052480. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904683 Free PMC article.
-
SSVEP unsupervised adaptive feature recognition method based on self-similarity of same-frequency signals.Front Neurosci. 2023 Aug 1;17:1161511. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1161511. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37600011 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalaganis F.P., Georgiadis K., Oikonomou V.P., Laskaris N.A., Nikolopoulos S., Kompatsiaris I. Unlocking the Subconscious Consumer Bias: A Survey on the Past, Present, and Future of Hybrid EEG Schemes in Neuromarketing. Front. Neuroergonomics. 2021;2:1–13. doi: 10.3389/fnrgo.2021.672982. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bin G., Gao X., Wang Y., Hong B., Gao S. VEP-based brain-computer interfaces: Time, frequency, and code modulations. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2009;4:22–26. doi: 10.1109/MCI.2009.934562. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

