Variants of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Vaccine Effectiveness
- PMID: 36298616
- PMCID: PMC9607623
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10101751
Variants of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Vaccine Effectiveness
Abstract
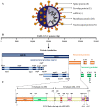
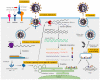
The incidence and death toll due to SARS-CoV-2 infection varied time-to-time; and depended on several factors, including severity (viral load), immune status, age, gender, vaccination status, and presence of comorbidities. The RNA genome of SARS-CoV-2 has mutated and produced several variants, which were classified by the SARS-CoV-2 Interagency Group (SIG) into four major categories. The first category; “Variant Being Monitored (VBM)”, consists of Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Gamma (P.1), Delta (B.1.617.2), Epsilon (B.1.427, B.1.429), Eta (B.1.525), Iota (B.1.526), Kappa (B.1.617.1), Mu (B.1.621), and Zeta (P.2); the second category; “Variants of Concern” consists of Omicron (B.1.1.529). The third and fourth categories include “Variants of Interest (VOI)”, and “Variants of High Consequence (VOHC)”, respectively, and contain no variants classified currently under these categories. The surge in VBM and VOC poses a significant threat to public health globally as they exhibit altered virulence, transmissibility, diagnostic or therapeutic escape, and the ability to evade the host immune response. Studies have shown that certain mutations increase the infectivity and pathogenicity of the virus as demonstrated in the case of SARS-CoV-2, the Omicron variant. It is reported that the Omicron variant has >60 mutations with at least 30 mutations in the Spike protein (“S” protein) and 15 mutations in the receptor-binding domain (RBD), resulting in rapid attachment to target cells and immune evasion. The spread of VBM and VOCs has affected the actual protective efficacy of the first-generation vaccines (ChAdOx1, Ad26.COV2.S, NVX-CoV2373, BNT162b2). Currently, the data on the effectiveness of existing vaccines against newer variants of SARS-CoV-2 are very scanty; hence additional studies are immediately warranted. To this end, recent studies have initiated investigations to elucidate the structural features of crucial proteins of SARS-CoV-2 variants and their involvement in pathogenesis. In addition, intense research is in progress to develop better preventive and therapeutic strategies to halt the spread of COVID-19 caused by variants. This review summarizes the structure and life cycle of SARS-CoV-2, provides background information on several variants of SARS-CoV-2 and mutations associated with these variants, and reviews recent studies on the safety and efficacy of major vaccines/vaccine candidates approved against SARS-CoV-2, and its variants.
Keywords: COVID-19; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; Variants Being Monitored; Variants of Concern; Variants of High Consequence; delta; vaccine efficacy; variants of interest.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 29 August 2021)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

