Pathogenicity of La Jolla Virus in Drosophila suzukii following Oral Administration
- PMID: 36298712
- PMCID: PMC9609637
- DOI: 10.3390/v14102158
Pathogenicity of La Jolla Virus in Drosophila suzukii following Oral Administration
Abstract
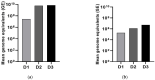
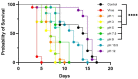
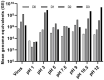
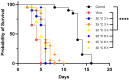
Drosophila suzukii (Ds) is an invasive pest insect that causes severe and widespread damage to soft fruit crops. Chemical control based on topical insecticides is inefficient and harmful to consumers and the environment, prompting interest in the development of biological control measures such as insect viruses with narrow host specificity. We previously described a strain of La Jolla virus (LJV) found in moribund Ds specimens in Germany. We demonstrated a pathogenic effect following the intrathoracic injection of LJV into adult Ds flies. However, the development of an effective biocontrol product based on LJV would require the characterization of (1) virulence following oral delivery, particularly in larvae, and (2) stability under different pH and temperature conditions reflecting realistic exposure scenarios. Here we describe the pathogenicity of LJV following oral delivery to Ds adults and larvae. The oral infection of Ds adults with LJV reduced survival in a concentration-dependent manner, whereas the oral infection of Ds larvae caused the arrest of development during pupation. LJV remained stable and infectious following exposure to a broad pH range and different temperatures. We, therefore, demonstrated that LJV is promising as a candidate biological control agent against Ds.
Keywords: Drosophila suzukii; Iflavirus; La Jolla virus (LJV); biological pest control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
La Jolla Virus: The Pathology and Transmission in Its Host Drosophila suzukii.Viruses. 2025 Mar 13;17(3):408. doi: 10.3390/v17030408. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40143335 Free PMC article.
-
Organization of the Structural Protein Region of La Jolla Virus Isolated from the Invasive Pest Insect Drosophila suzukii.Viruses. 2021 Apr 23;13(5):740. doi: 10.3390/v13050740. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33922699 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of natural viruses associated with the invasive insect pest Drosophila suzukii.J Invertebr Pathol. 2018 May;154:74-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 3. J Invertebr Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29625149
-
Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae): A Decade of Research Towards a Sustainable Integrated Pest Management Program.J Econ Entomol. 2021 Oct 13;114(5):1950-1974. doi: 10.1093/jee/toab158. J Econ Entomol. 2021. PMID: 34516634 Review.
-
Advances in the Chemical Ecology of the Spotted Wing Drosophila (Drosophila suzukii) and its Applications.J Chem Ecol. 2018 Oct;44(10):922-939. doi: 10.1007/s10886-018-1000-y. Epub 2018 Jul 27. J Chem Ecol. 2018. PMID: 30054769 Review.
Cited by
-
Global Trends in Research on Biological Control Agents of Drosophila suzukii: A Systematic Review.Insects. 2025 Jan 30;16(2):133. doi: 10.3390/insects16020133. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40003763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Reveals Virome Composition of Mosquitoes from a Transition Ecosystem of North-Northeast Brazil.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 14;14(7):1443. doi: 10.3390/genes14071443. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510347 Free PMC article.
-
La Jolla Virus: The Pathology and Transmission in Its Host Drosophila suzukii.Viruses. 2025 Mar 13;17(3):408. doi: 10.3390/v17030408. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40143335 Free PMC article.
-
Hunting Drosophila viruses from wild populations: A novel isolation approach and characterisation of viruses.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Mar 30;19(3):e1010883. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010883. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 36996192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haubrock P.J., Turbelin A.J., Cuthbert R.N., Novoa A., Taylor N.G., Angulo E., Ballesteros-Mejia L., Bodey T.W., Capinha C., Diagne C., et al. Economic costs of invasive alien species across Europe. NeoBiota. 2021;67:153–190. doi: 10.3897/neobiota.67.58196. - DOI
-
- Tait G., Mermer S., Stockton D., Lee J., Avosani S., Abrieux A., Anfora G., Beers E., Biondi A., Burrack H., et al. Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae): A Decade of Research Towards a Sustainable Integrated Pest Management Program. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021;114:1950–1974. doi: 10.1093/jee/toab158. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cini A., Ioriatti C., Anfora G. A review of the invasion of Drosophila suzukii in Europe and a draft research agenda for integrated pest management. Bull. Insectology. 2012;65:149–160.
-
- Bolda M.P., Goodhue R.E., Zalom F.G. Spotted Wing Drosophila: Potential Economic Impact of a Newly Established Pest. Univ. Calif. Giannini Found. Agric. Econ. 2010;13:5–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

