Transcriptome Analysis of Duck and Chicken Brains Infected with Aquatic Bird Bornavirus-1 (ABBV-1)
- PMID: 36298766
- PMCID: PMC9611670
- DOI: 10.3390/v14102211
Transcriptome Analysis of Duck and Chicken Brains Infected with Aquatic Bird Bornavirus-1 (ABBV-1)
Abstract
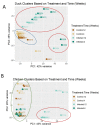
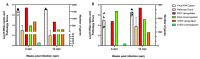
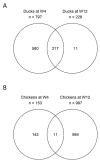
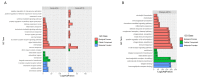
Aquatic bird bornavirus 1 (ABBV-1) is a neurotropic virus that infects waterfowls, resulting in persistent infection. Experimental infection showed that both Muscovy ducks and chickens support persistent ABBV-1 infection in the central nervous system (CNS), up to 12 weeks post-infection (wpi), without the development of clinical disease. The aim of the present study was to describe the transcriptomic profiles in the brains of experimentally infected Muscovy ducks and chickens infected with ABBV-1 at 4 and 12 wpi. Transcribed RNA was sequenced by next-generation sequencing and analyzed by principal component analysis (PCA) and differential gene expression. The functional annotation of differentially expressed genes was evaluated by gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis. The PCA showed that the infected ducks sampled at both 4 and 12 wpi clustered separately from the controls, while only the samples from the chickens at 12 wpi, but not at 4 wpi, formed a separate cluster. In the ducks, more genes were differentially expressed at 4 wpi than 12 wpi, and the majority of the highly differentially expressed genes (DEG) were upregulated. On the other hand, the infected chickens had fewer DEGs at 4 wpi than at 12 wpi, and the majority of those with high numbers of DEGs were downregulated at 4 wpi and upregulated at 12 wpi. The functional annotation showed that the most enriched GO terms were immune-associated in both species; however, the terms associated with the innate immune response were predominantly enriched in the ducks, whereas the chickens had enrichment of both the innate and adaptive immune response. Immune-associated pathways were also enriched according to the KEGG pathway analysis in both species. Overall, the transcriptomic analysis of the duck and chicken brains showed that the main biological responses to ABBV-1 infection were immune-associated and corresponded with the levels of inflammation in the CNS.
Keywords: GO; KEGG; aquatic bird birnavirus-1; bornaviruses; lncRNA; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental infection of aquatic bird bornavirus in Muscovy ducks.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 30;12(1):16398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20418-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36180525 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental infection of aquatic bird bornavirus 1 in domestic chickens.Vet Microbiol. 2022 Dec;275:109602. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109602. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Vet Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36395694
-
Isolation of Ontario aquatic bird bornavirus 1 and characterization of its replication in immortalized avian cell lines.Virol J. 2020 Jan 31;17(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-1286-6. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32005267 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental pathogenesis of aquatic bird bornavirus 1 in Pekin ducks.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 23;13(1):18094. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45205-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37872359 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental infection of aquatic bird bornavirus 1 (ABBV-1) in Canada geese (Branta canadensis).Vet Microbiol. 2024 Jan;288:109946. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2023.109946. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Vet Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38103394
Cited by
-
Multiomics analyses reveal high yield-related genes in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian/liver axis of chicken.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104276. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104276. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39299017 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of aquatic bird bornavirus 1 in turkeys of different age.Npj Viruses. 2025 Feb 24;3(1):14. doi: 10.1038/s44298-025-00095-z. Npj Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40295729 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Profiles of Pectoralis major Muscles Affected by Spaghetti Meat and Woody Breast in Broiler Chickens.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jan 5;14(2):176. doi: 10.3390/ani14020176. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delnatte P., Ojkic D., DeLay J., Campbell D., Crawshaw G., Smith D.A. Pathology and diagnosis of avian bornavirus infection in wild Canada geese (Branta canadensis), trumpeter swans (Cygnus buccinator) and mute swans (Cygnus olor) in Canada: A retrospective study. Avian Pathol. 2013;42:114–128. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2013.769669. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

