MNK1/2 contributes to periorbital hypersensitivity and hyperalgesic priming in preclinical migraine models
- PMID: 36299248
- PMCID: PMC10226734
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awac386
MNK1/2 contributes to periorbital hypersensitivity and hyperalgesic priming in preclinical migraine models
Abstract
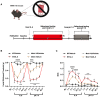
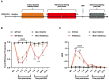
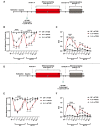
Migraine is thought to involve sensitization of the trigeminal nociceptive system. In preclinical pain models, activation of MNK-eIF4E signalling contributes to nociceptor sensitization and the development of persistent pain. Despite these observations, the role of MNK signalling in migraine remains unclear. Here, we investigate whether activation of MNK contributes to hypersensitivity in two rodent models of migraine. Female and male wild-type (WT) and MNK1 knock-out mice were subjected to repeated restraint stress or a dural injection of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tested for periorbital hypersensitivity and grimacing. Upon returning to baseline thresholds, stressed mice were administered a low dose of the nitric oxide donor sodium nitroprusside and mice previously injected with IL-6 were given a second dural injection of pH 7.0 to test for hyperalgesic priming. MNK1 knock-out mice were significantly less hypersensitive than the WT following dural IL-6 and did not prime to pH 7.0 or sodium nitroprusside. Furthermore, treatment with the selective MNK inhibitor, eFT508, in WT mice prevented hypersensitivity caused by dural IL-6 or pH 7.0. Together, these results implicate MNK-eIF4E signalling in the development of pain originating from the dura and strongly suggest that targeting MNK inhibition may have significant therapeutic potential as a treatment for migraine.
Keywords: MNK; eIF4E; headache; migraine; trigeminal.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
T.J.P. is a co-founder of 4E Therapeutics. J.L., T.J.P. and G.D. have filed for patent protection based on these findings.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ephrin-B2 promotes nociceptive plasticity and hyperalgesic priming through EphB2-MNK-eIF4E signaling in both mice and humans.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Aug;206:107284. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107284. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 38925462 Free PMC article.
-
De novo protein synthesis is necessary for priming in preclinical models of migraine.Cephalalgia. 2021 Feb;41(2):237-246. doi: 10.1177/0333102420970514. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Cephalalgia. 2021. PMID: 33200943
-
Peroxynitrite Contributes to Behavioral Responses, Increased Trigeminal Excitability, and Changes in Mitochondrial Function in a Preclinical Model of Migraine.J Neurosci. 2023 Mar 1;43(9):1627-1642. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1366-22.2023. Epub 2023 Jan 25. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36697259 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in developing MNK inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Jul 5;219:113420. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113420. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33892273 Review.
-
MNK, mTOR or eIF4E-selecting the best anti-tumor target for blocking translation initiation.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Nov 15;260:115781. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115781. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37669595 Review.
Cited by
-
Widespread hyperexcitability of nociceptor somata outlasts enhanced avoidance behavior after incision injury.Pain. 2025 May 1;166(5):1088-1104. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003443. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Pain. 2025. PMID: 39432803
-
Vinorelbine causes a neuropathic pain-like state in mice via STING and MNK1 signaling associated with type I interferon induction.iScience. 2024 Jan 8;27(2):108808. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108808. eCollection 2024 Feb 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38303713 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent changes in nociceptor translatomes govern hyperalgesic priming in mouse models.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 8:2024.08.07.606891. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.07.606891. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Pain. 2025 Jun 1;166(6):1395-1405. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003523. PMID: 39149295 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
ephrin-B2 promotes nociceptive plasticity and hyperalgesic priming through EphB2-MNK-eIF4E signaling in both mice and humans.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Aug;206:107284. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107284. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 38925462 Free PMC article.
-
Tomivosertib reduces ectopic activity in dorsal root ganglion neurons from patients with radiculopathy.Brain. 2024 Sep 3;147(9):2991-2997. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae178. Brain. 2024. PMID: 39046204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strassman AM, Raymond SA, Burstein R. Sensitization of meningeal sensory neurons and the origin of headaches. Nature. 1996;384:560–564. - PubMed
-
- Zhang XC, Strassman AM, Burstein R, Levy D. Sensitization and activation of intracranial meningeal nociceptors by mast cell mediators. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;322:806–812. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch T, Goadsby PJ. Increased responses in trigeminocervical nociceptive neurons to cervical input after stimulation of the dura mater. Brain. 2003;126:1801–1813. - PubMed
-
- Glock C, Heumüller M, Schuman EM. mRNA transport & local translation in neurons. Current Opinion Neurobiol. 2017;45:169–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

