A full-length transcriptome and gene expression analysis of three detoxification gene families in a predatory stink bug, Picromerus lewisi
- PMID: 36299261
- PMCID: PMC9589283
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1016582
A full-length transcriptome and gene expression analysis of three detoxification gene families in a predatory stink bug, Picromerus lewisi
Abstract
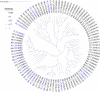
The predatory stink bug P. Lewisi shows potential for Integrated Pest Management programs for controlling Lepidoptera pest insects in crops and forests. The importance of this insect for biological control has stimulated several studies into its biology and ecology. However, P. lewisi has little genetic information available. In the present study, PacBio single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing and Illumina RNA-seq sequencing technologies were used to reveal the full-length transcriptome profiling and tissue-specific expression patterns of P. lewisi. A total of 12,997 high-quality transcripts with an average length of 2,292 bp were obtained from different stages of P. lewisi using SMRT sequencing. Among these, 12,101 were successfully annotated in seven public databases. A total of 67 genes of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases, 43 carboxylesterase genes, and 18 glutathione S-transferase genes were identified, most of which were obtained with full-length ORFs. Then, tissue-specific expression patterns of 5th instar nymphs were analyzed using Illumina sequencing. Several candidate genes related to detoxification of insecticides and other xenobiotics as well as the degradation of odors, were identified in the guts and antennae of P. lewisi. The current study offered in-depth knowledge to understand the biology and ecology of this beneficial predator and related species.
Keywords: Picromerus lewisi; carboxylesterase; cytochrome P450 monooxygenase; glutathione S-transferase; iso-seq; predatory stink bug.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Wang, Jiang, Yang, Li, Huang and He.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors ZL and CH were employed by Guizhou Provincial Tobacco Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Bailey E., Field L., Rawlings C., King R., Mohareb F., Pak K. H., et al. (2022). A scaffold-level genome assembly of a minute pirate bug, Orius laevigatus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae), and a comparative analysis of insecticide resistance-related gene families with hemipteran crop pests. BMC Genomics 23, 45. 10.1186/s12864-021-08249-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

