The circular RNA circ_0099630/miR-940/receptor-associated factor 6 regulation cascade modulates the pathogenesis of periodontitis
- PMID: 36299308
- PMCID: PMC9588814
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2022.04.005
The circular RNA circ_0099630/miR-940/receptor-associated factor 6 regulation cascade modulates the pathogenesis of periodontitis
Abstract
Background/purpose: Periodontitis is one of the highly prevalent chronic inflammatory conditions in adults. The importance of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in the regulation of inflammation has been gradually reported in recent years, but the role of circRNA circ_0099630 in periodontitis has not been reported.
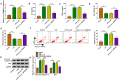
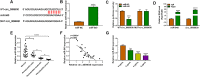
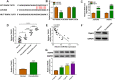
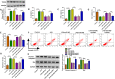
Materials and methods: The contents of circ_0099630, microRNA-940 (miR-940) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) were measured using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) or Western blot. Inflammatory factor secretion, cell proliferation, and apoptosis were analyzed under the application of Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8), 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) and flow cytometry, respectively. The Western blot also analyzed the phosphorylation levels of RELA proto-oncogene (P65) and IkappaBalpha (IκBα), key molecules of the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) pathway. The relationship between miR-940 and circ_0099630 or TRAF6 was verified by luciferase reporter system and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay.
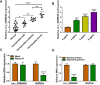
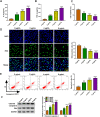
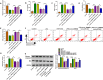
Results: Higher abundance of circ_0099630 and TRAF6 and lower miR-940 expression were observed in periodontitis, and circ_0099630 knockdown attenuated the damage of human PDL cells (PDLCs) induced by lipopolysaccharides (LPS). The relationship between miR-940 and circ_0099630 or TRAF6 was evidenced, while miR-940 downregulation diminished the repair effect of si-circ_0099630 on overexpression LPS-induced damage in PDLCs. Similarly, TRAF6 upregulation impaired the mitigating effect of miR-940 overexpression on LPS-induced injury in PDLCs. Circ_0099630 silencing evidently curbed the phosphorylation levels of P65 and IκBα and thus attenuating the inflammatory response by acting on the miR-940/TRAF6 axis.
Conclusion: Silencing circ_0099630 alleviates LPS-induced periodontal ligament cell injury via targeting miR-940/TRAF6/NF-κB in periodontitis.
Keywords: 3′UTRs, 3′ untranslated regions; ATG14, autophagy related 14; CCK8, Cell Counting Kit-8; Cdr1as, circRNA CDR1 antisense RNA; Circ_0099630; ELISA, Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; EdU, 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine; FOXM1, forkhead box M1; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; MiR-940; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; PDLCs, periodontal ligament cells; Periodontitis; RIP, RNA immunoprecipitation; RIPA, radioimmune precipitation assay; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRAF6; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; U6, U6 small nuclear RNA; ceRNA, competing endogenous RNA; circRNAs, circular RNAs; miR-940, microRNA-940; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
© 2022 Association for Dental Sciences of the Republic of China. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circ_0114427 promotes LPS-induced septic acute kidney injury by modulating miR-495-3p/TRAF6 through the NF-κB pathway.Autoimmunity. 2022 Feb;55(1):52-64. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2021.1995861. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Autoimmunity. 2022. PMID: 34730059
-
KNOCKDOWN OF CIRC_0114428 ALLEVIATES LPS-INDUCED HK2 CELL APOPTOSIS AND INFLAMMATION INJURY VIA TARGETING MIR-215-5P/TRAF6/NF-ΚB AXIS IN SEPTIC ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY.Shock. 2024 Apr 1;61(4):620-629. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002245. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Shock. 2024. PMID: 38010029
-
Circ_0138959/miR-495-3p/TRAF6 axis regulates proliferation, wound healing and osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells in periodontitis.J Dent Sci. 2022 Jul;17(3):1125-1134. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2022.01.010. Epub 2022 Feb 15. J Dent Sci. 2022. PMID: 35784154 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0003575 knockdown alleviates ox-LDL-induced human aortic endothelial cell dysfunction in atherosclerosis by miR-637/TRAF6 axis.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2023;85(2):173-187. doi: 10.3233/CH-231858. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2023. PMID: 37599528
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Associated Factor 6 and Human Cancer: A Systematic Review of Mechanistic Insights, Functional Roles, and Therapeutic Potential.J Cancer. 2024 Jan 1;15(2):560-576. doi: 10.7150/jca.90059. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38169510 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impacts of Circular RNAs on the Osteogenic Differentiation of Dental Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2025 May 8;2025:8338337. doi: 10.1155/sci/8338337. eCollection 2025. Stem Cells Int. 2025. PMID: 40376229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expression Patterns of Non-Coding RNAs in Periodontal Disease.Dent J (Basel). 2024 May 24;12(6):159. doi: 10.3390/dj12060159. Dent J (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38920860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extraction of coronary thrombus-derived exosomes from patients with acute myocardial infarction and its effect on the function of adventitial cells.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 16;20(1):e0313582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313582. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39820800 Free PMC article.
-
Potential protective effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A network-based pharmacological and molecular docking study.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Jul 6;18(1):20230746. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0746. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 37533739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slots J. Periodontitis: facts, fallacies and the future. Periodontol 2000. 2017;75:7–23. - PubMed
-
- Contreras A., Moreno S.M., Jaramillo A., et al. Periodontal microbiology in Latin America. Periodontol 2000. 2015;67:58–86. - PubMed
-
- Botero J.E., Vidal C., Contreras A., Parra B. Comparison of nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR), real-time PCR and viral culture for the detection of cytomegalovirus in subgingival samples. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2008;23:239–244. - PubMed
-
- Li X., Sun Q.F., Sun Y.D., Ge S.H., Yang P.S. Quantitative detection of human cytomegalovirus in aggressive and chronic periodontitis lesions. Hua xi kou qiang yi xue za zhi. 2011;29:242–245. - PubMed
-
- Papapanou P.N., Susin C. Periodontitis epidemiology: is periodontitis under-recognized, over-diagnosed, or both? Periodontol 2000. 2017;75:45–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

