Profile of dental use for diseases of pulp and periapical tissues under the National Health Insurance system in Taiwan in 2020
- PMID: 36299341
- PMCID: PMC9588822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2022.08.023
Profile of dental use for diseases of pulp and periapical tissues under the National Health Insurance system in Taiwan in 2020
Abstract
Background/purpose: The penetration rate of National Health Insurance (NHI) of Taiwan is as high as 99.9%. This study investigated the profile of dental use for diseases of pulp and periapical tissues under the NHI system of Taiwan in 2020.
Materials and methods: Data on the population and medical records of the NHI system were obtained from the websites of Ministry of the Interior and the NHI Administration, respectively. The dental patient data were divided into 18 age groups to analyze dental treatment records claimed in 2020.
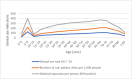
Results: Under the NHI system in Taiwan in 2020, the dental use rate for treatment of diseases of pulp and periapical tissues had the highest peak (12.76%) in the 5-9-year age group. It dropped abruptly to the lowest point (2.71%) in the 10-14-year age group, raised gradually with increasing age, reached to the second and third highest peaks in the 70-74-year (10.75%) and 65-69-year (10.72%) age groups, respectively, and finally declined to 4.40% in the greater than 85-year age group. Furthermore, the number of out-patient visits per 1000 people and the medical expenses per person for diseases of pulp and periapical tissues among the same 18 age groups also showed a similar trend to the dental use rate.
Conclusion: Diseases of pulp and periapical tissues are still the main diseases of the oral cavity. From a cost-effectiveness viewpoint, Taiwan government should develop a better oral health care policy to prevent dental caries from deteriorating into diseases of pulp and periapical tissues for all citizens.
Keywords: Dental use rate; Diseases of pulp and periapical tissues; Endodontic diseases; National Health Insurance.
© 2022 Association for Dental Sciences of the Republic of China. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures

References
-
- Moiseiwitsch J.R.D., Trope M. Nonsurgical root canal therapy treatment with apparent indications for root-end surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;86:335–340. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health and Welfare . Ministry of Health and Welfare; Taipei, Taiwan: 2021. The 2020 national health insurance medical statistics. [In Chinese]
-
- Hugoson A., Koch G. Oral health in 1000 individuals aged 3–70 years in the community of Jönköping, Sweden: a review. Swed Dent J. 1979;3:69–87. - PubMed
-
- Hull T.E., Robertson P.B., Steiner J.C., del Aguila M.A. Patterns of endodontic care for a Washington state population. J Endod. 2003;29:553–556. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

