Phase I studies of BI 1015550, a preferential phosphodiesterase 4B inhibitor, in healthy males and patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 36299369
- PMCID: PMC9589333
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00240-2022
Phase I studies of BI 1015550, a preferential phosphodiesterase 4B inhibitor, in healthy males and patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Introduction: BI 1015550 is a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor that has antifibrotic properties. Phase I and Ic studies were conducted to investigate the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of BI 1015550 in healthy male subjects and patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
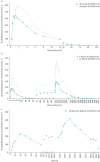
Methods: In the phase I study, 42 subjects were partially randomised to receive placebo or BI 1015550 in single rising doses of 36 mg and 48 mg, or multiple rising doses of 6 mg and 12 mg twice daily over 14 days. In the phase Ic study, 15 patients with IPF were randomised to receive 18 mg BI 1015550 or placebo twice daily for up to 12 weeks. For both studies, the primary endpoint was the number of subjects with drug-related adverse events (AEs).
Results: In the Phase I study, drug-related AEs were reported for 50.0% of healthy male subjects treated with a single dose of BI 1015550, compared with 16.7% receiving placebo. For those receiving multiple doses, drug-related AEs were reported for 37.5% of those treated with BI 1015550 and 12.5% receiving placebo. The most frequently reported AEs by organ class were nervous system disorders, which were largely driven by headache. In the Phase Ic study, drug-related AEs were reported in 90.0% of patients treated with BI 1015550, compared with 60.0% of those receiving placebo. The most frequent AEs by organ class were gastrointestinal AEs.
Conclusions: BI 1015550 had an acceptable safety profile in healthy male subjects and male and female patients with IPF, supporting further development in larger trials.
Copyright ©The authors 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: T.M. Maher has received consultancy fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche/Genentech, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Blade Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Galecto, GlaxoSmithKline, IQVIA, Pliant, Respivant, Theravance and Veracyte; and honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim and Roche/Genentech. C. Schlecker, D. Leudtke, S. Bossert and D.F. Zoz are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. A. Schultz is an employee of CRS Clinical Research Services Mannheim GmbH.
Figures

References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration . Ofev® (nintedanib): prescribing information. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/205832s014lbl.pdf Date last accessed: 12 January 2022.
-
- European Medicines Agency . OFEV® (nintedanib): summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/ofev-epar-pro... Date last accessed: 26 April 2021.
-
- US Food and Drug Administration . ESBRIET® (pirfenidone) prescribing information. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/022535s012,208... Date last accessed: 12 March 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
