Associations between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, body mass index and body fat composition among Emirati population: Results from the UAE healthy future study
- PMID: 36299461
- PMCID: PMC9589411
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.954300
Associations between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, body mass index and body fat composition among Emirati population: Results from the UAE healthy future study
Abstract
Introduction: Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency are highly prevalent among several populations across the globe. Numerous studies have shown a significant correlation between body-mass-index (BMI) and Vitamin D status, however, some results differed according to ethnicity. Despite the abundance of sunshine throughout the year, vitamin D deficiency is prominent in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). In this study, we analyzed the UAE Healthy Future Study (UAEHFS) pilot data to investigate the association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) and % body fat (BF) composition as well as BMI.
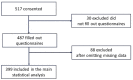
Material and methods: Data from a total of 399 Emirati men and women aged ≥ 18 years were analyzed. Serum 25(OH)D and standard measures of weight and height were included in the analyses. Vitamin D deficiency was defined as serum 25(OH)D concentration<20 ng/ml. Multivariate quantile regression models were performed to explore the relationship between serum 25(OH)D levels and % BF composition and BMI correspondingly.
Results: There were 281 (70.4%) males and 118 (29.6%) females included in this study. More than half of the study participants had vitamin D insufficiency (52.4%), and nearly a third had vitamin D deficiency (30.3%); while only 17.3% had optimal levels. A statistically significant negative association between serum 25(OH) D levels and % BF composition was observed at intermediate percentiles while a statistically significant negative association between serum 25(OH)D and BMI was only observed at the median (50th percentile).
Conclusion: The study findings support the association between low serum 25(OH) D levels (low vitamin D status) and high % BF composition and high BMI among adult Emiratis. Further longitudinal data from the prospective UAEHFS could better elucidate the relationship between serum 25(OH) D levels, % BF composition, and BMI in the context of various health outcomes among this population.
Keywords: body fat; body mass index; quantile regression; serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2022 AlAnouti, Ahmad, Wareth, Dhaheri, Oulhaj, Junaibi, Naeemi, Hamiz, Hosani, Zaabi, Mezhal, Maskari, Alsafar, Yaaqoub, Bastaki, Houqani, Oumeziane, Juber, Sherman, Shah, Alsharid, Zaabi, Loney, Mahmeed, Abdulle and Ali.
Conflict of interest statement
MB and NO were employed by Abu Dhabi Health Services Company, SEHA. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lips P, Cashman KD, Lamberg-Allardt C, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Bianchi ML, et al. Current vitamin d status in European and middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin d deficiency: a position statement of the European calcified tissue society. Eur J Endocrinol (2019) 180(4):P23–54. doi: 10.1530/EJE-18-0736 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buckley AJ, Barakat MT, Holick MF, Lessan N. Parameters of bone and cardiovascular health related to 25-hydroxyvitamin d status in emirati nationals attending primary care and diabetes services: a retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep (2019) 9(1):1–8. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40523-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

