Cellular Landscaping of COVID-19 and Gynaecological Cancers: An Infrequent Correlation
- PMID: 36299504
- PMCID: PMC9592241
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5231022
Cellular Landscaping of COVID-19 and Gynaecological Cancers: An Infrequent Correlation
Abstract
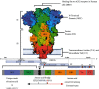
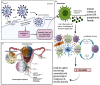
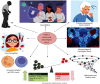
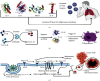
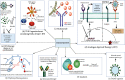
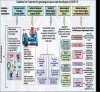
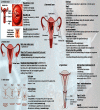
COVID-19 resulted in a mortality rate of 3-6% caused by SARS-CoV-2 and its variant leading to unprecedented consequences of acute respiratory distress septic shock and multiorgan failure. In such a situation, evaluation, diagnosis, treatment, and care for cancer patients are difficult tasks faced by medical staff. Moreover, patients with gynaecological cancer appear to be more prone to severe infection and mortality from COVID-19 due to immunosuppression by chemotherapy and coexisting medical disorders. To deal with such a circumtances oncologists have been obliged to reconsider the entire diagnostic, treatment, and management approach. This review will provide and discuss the molecular link with gynaecological cancer under COVID-19 infection, providing a novel bilateral relationship between the two infections. Moreover, the authors have provided insights to discuss the pathobiology of COVID-19 in gynaecological cancer and their risks associated with such comorbidity. Furthermore, we have depicted the overall impact of host immunity along with guidelines for the treatment of patients with gynaecological cancer under COVID-19 infection. We have also discussed the feasible scope for the management of COVID-19 and gynaecological cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Rahul Bhattacharjee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cancer and COVID-19: Unmasking their ties.Cancer Treat Rev. 2020 Aug;88:102041. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102041. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020. PMID: 32516704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ESMO management and treatment adapted recommendations in the COVID-19 era: gynaecological malignancies.ESMO Open. 2020 Jul;5(Suppl 3):e000827. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2020-000827. ESMO Open. 2020. PMID: 32718919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High dose dexamethasone treatment for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome secondary to COVID-19: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Aug 26;21(1):743. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04646-y. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32843098 Free PMC article.
-
Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 11;22(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04998-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33430924 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis Care Pathway 2019.Qatar Med J. 2019 Nov 7;2019(2):4. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2019.qccc.4. eCollection 2019. Qatar Med J. 2019. PMID: 31763206 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

