Efficacy and safety of CO2 cryotherapy in the treatment of infants with tracheobronchial tuberculosis
- PMID: 36299689
- PMCID: PMC9591804
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.984738
Efficacy and safety of CO2 cryotherapy in the treatment of infants with tracheobronchial tuberculosis
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of CO2 cryotherapy for lymph node fistula tracheobronchial tuberculosis (TBTB) in infants.
Patients and methods: A retrospective analysis was undertaken on seven patients with lymph node fistula tracheobronchial tuberculosis who underwent fiberoptic bronchoscopy (FB) interventional therapy in the respiratory department of Tianjin Children's Hospital from July 2012 to July 2020. The efficacy, safety, and prognosis of CO2 cryotherapy intervention for the treatment of lymph node fistula TBTB in infants were summarized and analyzed.
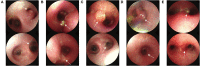
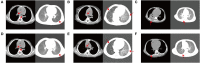
Results: Seven patients with lymph node fistula TBTB were included in this study. Their ages ranged from 6-13 months. The course of the disease from onset to TBTB ranged from 20 to 70 days. The pathological diagnoses of seven cases by FB combined with tissue biopsy were lymph node fistula TBTB, of which 28.57% (two cases) were in the early stage of rupture and 71.43% (five cases) were in the rupture stage. All patients were treated with CO2 cryotherapy combined with foreign body forceps and local injection drugs based on systemic antituberculosis chemotherapy. Two patients were treated once with CO2 cryotherapy, and five were treated three times. According to the comparison of the clinical symptoms, imaging results, and endoscopic presentations before and after the intervention, six patients achieved clinical cure, and one achieved clinical improvement. No severe intraoperative or postoperative complications were observed. The clinical symptoms, endoscopic findings, radiological manifestations, and quality of life of all patients showed marked improvement. No recurrence occurred after 3-6 months of follow-up with FB.
Conclusion: CO2 cryotherapy can improve the treatment effect of lymph node fistula in infants with TBTB and reduce the incidence of complications. This treatment is safe and reliable in infants.
Keywords: CO2 cryotherapy; bronchoscopy; infants; lymph node fistula; tracheobronchial tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Zhang, Yang, Xu and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Clinical application of transbronchial cryotherapy in the diagnosis and treatment of tracheobronchial tuberculosis in children].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Nov 2;59(11):963-967. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20210504-00378. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34711032 Chinese.
-
Multidrug resistant lymph node fistula tracheobronchial tuberculosis: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Dec;98(49):e18288. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018288. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31804372 Free PMC article.
-
[Classification of tracheobronchial tuberculosis in 252 children].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2022 Mar 12;45(3):282-288. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20210624-00444. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35279992 Chinese.
-
Tracheobronchial tuberculosis.J Thorac Dis. 2016 Dec;8(12):3818-3825. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.12.75. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 28149582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Bronchoesophageal fistula secondary to mediastinal lymph node tuberculosis: a case report and review of the literature].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2013 Nov;36(11):829-932. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24507394 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Progress in the Application of Bronchoscopic Cryotherapy in Pediatric Pulmonary Diseases.Children (Basel). 2024 Sep 18;11(9):1130. doi: 10.3390/children11091130. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334662 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

