Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Review
- PMID: 36299969
- PMCID: PMC9587755
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.29458
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Review
Abstract
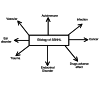
The objective of this review is to present and evaluate the current views on sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss is an otolaryngology emergency requiring immediate diagnosis and treatment. The etiology of the majority of cases is unknown. The etiology can be classified into various categories such as autoimmune diseases, infections, functional, metabolic disorders, vascular disorders, traumatic causes, due to toxins, and neurological disorders. We searched the U.S. National Library of Medicine's PubMed database using the terms "sudden S.N.H.L.," "virus and ssnhl," and "sudden deafness," as well as the keywords such as "etiology," "COVID 19, and ssnhl," "epidemiology," "clinical characteristics," "management," "therapy," and "prognosis."
Keywords: covid 19 and hearing loss; emergency in e.n.t; sudden hearing impairment; sudden sensorineural hearing loss; hearing loss.
Copyright © 2022, Tripathi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Clinical associations of serum antiendothelial cell antibodies in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cadoni G, Agostino S, Manna R, De Santis A, Fetoni AR, Vulpiani P, Ottaviani F. Laryngoscope. 2003;113:797–801. - PubMed
-
- Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Chau JK, Lin JR, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD. Laryngoscope. 2010;120:1011–1021. - PubMed
-
- The relationship of the herpesvirus family to sudden hearing loss: a prospective clinical study and literature review. Wilson WR. Laryngoscope. 1986;96:870–877. - PubMed
-
- Sudden deafness and Lyme disease. Lorenzi MC, Bittar RS, Pedalini ME, Zerati F, Yoshinari NH, Bento RF. Laryngoscope. 2003;113:312–315. - PubMed
-
- The clinical assessment, treatment, and prevention of lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Wormser GP, Dattwyler RJ, Shapiro ED, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:1089–1134. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources