Protective effects of silibinin on LPS-induced inflammation in human periodontal ligament cells
- PMID: 36300030
- PMCID: PMC9591103
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1019663
Protective effects of silibinin on LPS-induced inflammation in human periodontal ligament cells
Abstract
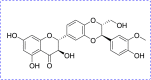
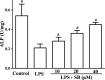
Clinically, periodontitis is a chronic nonspecific inflammation that leads to damaged teeth and their supporting gum tissues. Although many studies on periodontitis have been conducted, therapy with natural products is still rare. Silibinin has been proven to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. However, the effects of silibinin on lipopolyssacharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in periodontal ligaments (PDLs) have not yet been investigated. In this study, the PDLs were treated with silibinin (10, 20, and 40 μM) in the presence of LPS. The results showed that silibinin treatment reduced the levels of NO, PGE2, IL-6, TNF-α, MMP-1, and MMP-3 and enhanced the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH). Moreover, silibinin treatment downregulated RANKL levels and upregulated OPG and ALP levels. In summary, silibinin protected PDLs against LPS-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and osteogenic differentiation.
Keywords: LPS-induced; human periodontal ligament cells; inflammation; protective effects; silibinin.
Copyright © 2022 Meng, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Bae W. J., Park J. S., Kang S. K., Kwon I. K., Kim E. C. (2018). Effects of melatonin and its underlying mechanism on ethanol-stimulated senescence and osteoclastic differentiation in human periodontal ligament cells and cementoblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1742. 10.3390/ijms19061742 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

