Application of novel Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures as an antimicrobial agent and magnetic nanocatalyst in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds
- PMID: 36300031
- PMCID: PMC9589061
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1014731
Application of novel Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures as an antimicrobial agent and magnetic nanocatalyst in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds
Abstract
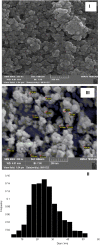
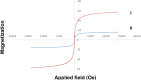
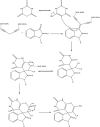
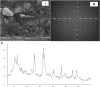
Using the microwave-assisted method, novel Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures were synthesized. The crystallinity, thermal stability, adsorption/desorption isotherms, morphology/size distribution, and magnetic hysteresis of synthesized Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures were characterized by XRD patterns, TGA curve, BET adsorption/desorption technique, SEM image, and VSM curve, respectively. After confirming the Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures, its antimicrobial properties against Gram-positive bacterial, Gram-negative bacterial, and fungal strains based on minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC), and minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) values were studied. The MIC values in antimicrobial activity for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains, between 16-128 μg/ml, and for fungal strain, 128 μg/ml were observed. The results showed that the high specific surface area of Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures caused the antimicrobial power of nanoparticles to be high, and the observed antimicrobial effects were higher than some known commercial antimicrobial drugs. Another advantage of the specific surface area of Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures was its high catalytic properties in the three-component reaction of isatin, malononitrile, and dimedone. New spiro [indoline-pyranopyrimidines] derivatives were synthesized with high efficiency. The catalytic activity results of Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures showed that, in addition to recyclability, derivatives could be synthesized in less time than previously reported methods. The results of investigating the catalytic activity of Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures showed that the spiro [indoline-pyranopyrimidines] derivatives were synthesized in the time range of 10-20 min with an efficiency of over 85%. As a final result, it can be concluded that the microwave synthesis method improves the unique properties of magnetic nanostructures, especially its specific surface area, and has increased its efficiency.
Keywords: Fe3O4/Zn-metal organic framework magnetic nanostructures; MIC and MBC value; antimicrobial agent; microwave assisted; spiro[indoline-pyranopyrimidines.
Copyright © 2022 Bashar, Kareem, Hasan, Ahmad, Alshehri, Al-Majdi, Hadrawi, AL Kubaisy and Qasim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Abdieva G. A., Patra I., Al-Qargholi B., Shahryari T., Chauhan N. P. S., Moghaddam-Manesh M. (2022). An efficient ultrasound-assisted synthesis of Cu/Zn hybrid MOF nanostructures with high microbial strain performance. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 861580. 10.3389/fbioe.2022.861580 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad N., Almahdawi S., Alshehri A., Shkir M., Ahmad I., Hasan P., et al. (2022). Facile low temperature synthesis of homogeneous CuS nanosheets: An effect of Ga loading on structural, optical, nonlinear and antimicrobial properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 277, 125552. 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125552 - DOI
-
- Ahmad N., Alshehri A., Ahmad I., Shkir M., Hasan P., Melaibari A. A. (2021). In doping effect on the structural, morphological, optical and enhanced antimicrobial activity of facilely synthesized novel CuS nanostructures. Surfaces Interfaces 27, 101536. 10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101536 - DOI
-
- Al-Obaidi Z. M. J., Hussein Y. A., Al-Duhaidahawi D., Al-Aubaidy H. A., et al. (2022). Molecular docking studies and biological evaluation of luteolin on cerebral ischemic reperfusion injury. Egypt. J. Chem. 65, 1–2. 10.21608/ejchem.2021.106753.4898 - DOI
-
- Al-Rowaili F. N., Jamal A., Ba-Shammakh M. S., Rana A. (2018). A review on recent advances for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to methanol using metal–organic framework (MOF) and non-MOF catalysts: Challenges and future prospects. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6, 15895–15914. 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03843 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

