The factors that affect members' use of a beauty industry matchmaking platform: Validation of the COM-B extended model
- PMID: 36300047
- PMCID: PMC9588966
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.976109
The factors that affect members' use of a beauty industry matchmaking platform: Validation of the COM-B extended model
Abstract
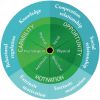
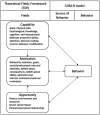
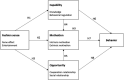
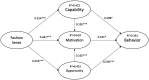
The global impact of COVID-19 has seriously affected health and livelihood in every country or region, especially in terms of physical consumption behaviors. Hairdressing is an essential physical consumption behavior. To prevent infection, the consumption model for using the beauty industry matchmaking platform (BIMP) has been used during the pandemic. This study investigates the changes in the behavior of media app users in the beauty industry in the post-epidemic era of COVID-19. The COM-B model is the basis for a research framework to study the factors that affect changes in behavior in the areas of Capability, Motivation, and Opportunity of the theoretical framework. A new dimension of fashion sense has expanded the application and validation of the COM-B model to determine the causal relationship between the ability to pursue beauty, motivation, fashion sense, and opportunities by using the platform and the dimension of user behavior. The study finds that fashion sense in the BIMP has a positive and significant impact on beauty care ability, self-motivation to pursue beauty and future cooperation opportunities. The ability, motivation and opportunity to act are all positively significant, which is in agreement with the theoretical framework of the COM-B model. There is no mediating effect for motivation between fashion sense and behavior. The results of this study show that increasing the sense of fashion for members using the BIMP will increases active behavior for members using the platform. This study also proposes practical suggestions for the operation of the BIMP based on the results.
Keywords: COM-B; COVID-19; beauty industry matchmaking platform; behavioral change; fashion sense.
Copyright © 2022 Chang and Hsu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abd Rahman A., Asrarhaghighi E., Ab Rahman S. (2015). Consumers and halal cosmetic products: knowledge, religiosity, attitude and intention. J. Islam. Mark. 6, 148–163. doi: 10.1108/JIMA-09-2013-0068 - DOI
-
- Ajzen I. (1985). “From intentions to actions: a theory of planned behavior,” in Action control. (eds.) J. Kuhl and J. Beckmann (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; ), 11–39.
-
- Ajzen I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process:50
-
- Ajzen I., Fishbein M. (1975). A Bayesian analysis of attribution processes. Psychol. Bull. 82, 261–277. doi: 10.1037/h0076477 - DOI
-
- Atkins L., Michie S. (2013). Changing eating behaviour: what can we learn from behavioural science? Nutr. Bull. 38, 30–35. doi: 10.1111/nbu.12004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources