ATF6α contributes to rheumatoid arthritis by inducing inflammatory cytokine production and apoptosis resistance
- PMID: 36300114
- PMCID: PMC9590309
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.965708
ATF6α contributes to rheumatoid arthritis by inducing inflammatory cytokine production and apoptosis resistance
Abstract
Objective: The contribution of activating transcription factor 6α (ATF6α) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis, especially on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs), has been suggested by its sensitivity to inflammatory stimulus. However, the exact role and therapeutic potential of ATF6α in RA remains to be fully elucidated.
Methods: ATF6α expression was determined in joint tissues and FLS, and gain-of-function and loss-of-function analyses were applied to evaluate the biological roles of ATF6α in RA FLSs. A murine collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model, combining both gene deletion of ATF6α and treatment with the ATF6α inhibitor Ceapin-A7, was employed. Joint inflammation, tissue destruction, circulating levels of inflammatory cytokines were assessed in CIA mice. Transcriptome sequencing analysis (RNASeq), molecular biology, and biochemical approaches were performed to identify target genes of ATF6α.
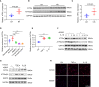
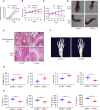
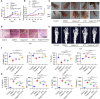
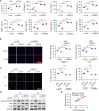
Results: ATF6α expression was significantly increased in synovium of RA patients and in synovium of mice subjected to CIA. ATF6α silencing or inhibition repressed RA FLSs viability and cytokine production but induced the apoptosis. CIA-model mice with ATF6α deficiency displayed decreased arthritic progression, leading to profound reductions in clinical and proinflammatory markers in the joints. Pharmacological treatment of mice with Ceapin-A7 reduced arthritis severity in CIA models. RNA-sequencing of wild-type and knockdown of ATF6α in RA FLSs revealed a transcriptional program that promotes inflammation and suppresses apoptosis, and subsequent experiments identified Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 3 (BIRC3) as the direct target for ATF6α.
Conclusion: This study highlights the pathogenic role of ATF6α-BIRC3 axis in RA and identifies a novel pathway for new therapies against RA.
Keywords: ATF6α; BIRC3; apoptosis resistance; inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis; unfolded protein response.
Copyright © 2022 Ge, Wang, Shi, Geng, Fan, Zhang, Zhang, Zhao, Li, Li, Shi, Song, Pan, Wang and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epigenetic Regulatory Axis MIR22-TET3-MTRNR2L2 Represses Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte-Mediated Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024 Jun;76(6):845-856. doi: 10.1002/art.42795. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38221658
-
Regulation of apoptosis and inflammatory responses by insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes and experimental animal models of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Apr;66(4):863-73. doi: 10.1002/art.38303. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24757139
-
Nitidine chloride inhibits fibroblast like synoviocytes-mediated rheumatoid synovial inflammation and joint destruction by targeting KCNH1.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt A):108273. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108273. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34700130
-
The p53 status in rheumatoid arthritis with focus on fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Immunol Res. 2021 Jun;69(3):225-238. doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09202-7. Epub 2021 May 13. Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33983569 Review.
-
Role of Sirtuins in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 12;24(2):1532. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021532. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675041 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole-Blood RNA Sequencing Profiling of Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated With Tofacitinib.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;7(7):e11761. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11761. Epub 2025 May 19. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40388487 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing Fibrosis Genes as Biomarkers of Ulcerative Colitis: A Bioinformatics Study Based on ScRNA and Bulk RNA Datasets.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025;25(9):710-720. doi: 10.2174/0118715303332155240912050838. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39428941 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-specific gene networks and drivers in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 5;15:1428773. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1428773. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39161769 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of 18F-FAPI-04 Imaging in Assessing the Therapeutic Response of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Mol Imaging Biol. 2023 Aug;25(4):630-637. doi: 10.1007/s11307-023-01817-6. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Mol Imaging Biol. 2023. PMID: 37020126
-
Growth hormone - releasing hormone in the immune system.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2025 Jun;26(3):457-466. doi: 10.1007/s11154-024-09913-w. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 39370499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

